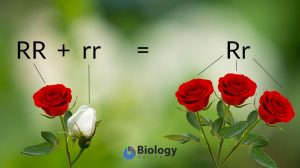Definition
adjective
(genetics) Of, or pertaining to, a gene (or allele) whose phenotypic expression is masked by a dominant gene (or allele)
(general) Going back; receding
noun
(1) A recessive gene, allele or trait
(2) An organism whose recessive trait is discernible or expressed
Supplement
In genetics, recessive may pertain to or describe a gene, an allele, or an organism based on dominance. Dominance pertains to the property of a gene (or allele) in relation to other genes or alleles. A gene or allele shows dominance when it suppresses the expression, or dominates the effects, of the recessive gene (or allele). According to Gregor Mendel’s Law of Dominance, when two alleles of an inherited pair is heterozygous, then, the allele that is expressed is dominant whereas the allele that is not expressed is recessive. A recessive gene or allele is one in which the effect is not tangible, or is masked by the effects of the dominant gene. The recessive trait may be expressed when the recessive genes are in homozygous condition or when the dominant gene is not present. That happens when an organism inherits a pair of recessive genes from its parents.
Word origin: Latin recess(us), a withdrawal, receding part + –ive
Compare:
See also:
Related term(s):
- autosomal recessive
- recessive gene
- recessive inheritance
- sex linked recessive
Related form(s):
- recessiveness (noun)
- recessively (adverb)