A developed system of roots.The network of underground roots and other plant structures found below ground level.
You will also like...

Plant Water Regulation
Plants need to regulate water in order to stay upright and structurally stable. Find out the different evolutionary adaptations of plants in terms of structure (e.g. stomata) and physiological mechanisms (e.g. root pressure, capillarity, transpiration pull, curving of leaves, etc.) that enabled them to maintain the appropriate water level...

Growth and Plant Hormones
Plants, like animals, produce hormones to regulate plant activities, including growth. They need these hormones to respond well to their environment and to sustain growth, development, and dispersal. Plant biologists recognize five major groups of plant hormones: auxins, gibberellins, ethylene, cytokinins, and abscisic acid. Find out in this guide the importance of each hormone in the life of a plant...
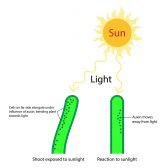
Plant Auxins – Phototropism & Geotropism
Plants produce hormones to regulate their growth. Auxins, for instance, influence plant growth. Know the role of auxin in plant growth and development in this tutorial...

Plant Tissues
Plant organs are comprised of tissues working together for a common function. The different types of plant tissues are meristematic, simple, secretory, and complex tissues. Find out the distinctive characteristics of each tissue in terms of structure and function...

Fruits, Flowers, and Seeds
This tutorial deals with the structure and function of flowers, fruits, and seeds. Also included here are the types of fruits, fruit dispersal mechanisms, and seed germination. The distinctions between dicots and monocots, the two major groups of flowering plants, are presented in this tutorial...

