shank
To fall off, as a leaf, flower, or capsule, on account of disease affecting the supporting footstalk; usually followed by off.
(Science: zoology) See Chank.
1. The part of the leg from the knee to the foot; the shin; the shin bone; also, the whole leg. His youthful hose, well saved, a world too wide For his shrunk shank. (Shak)
2. Hence, that part of an instrument, tool, or other thing, which connects the acting part with a handle or other part, by which it is held or moved. Specifically: That part of a key which is between the bow and the part which enters the wards of the lock.
The middle part of an anchor, or that part which is between the ring and the arms.
That part of a hoe, rake, knife, or the like, by which it is secured to a handle.
A loop forming an eye to a button.
3. The space between two channels of the doric triglyph.
4. A large ladle for molten metal, fitted with long bars for handling it.
5. The body of a type.
6. The part of the sole beneath the instep connecting the broader front part with the heel.
7. (Science: zoology) A wading bird with long legs; as, the green-legged shank, or knot; the yellow shank, or tattler; called also shanks.
8. Flat-nosed pliers, used by opticians for nipping off the edges of pieces of glass to make them round. Shank painter, a short rope or chain which holds the shank of an anchor against the side of a vessel when it is secured for a voyage. To ride shank’s mare, to go on foot; to walk.
Origin: OE. Shanke, schanke, schonke, AS. Scanca, sceanca, sconca, sceonca; akin to D. Schonk a bone, G. Schenkel thigh, shank, schinken ham, OHG. Scincha shank, Dan. & Sw. Skank. Cf. Skink.
Dictionary > Shank
You will also like...

Movement of Molecules Across Cell Membranes
Molecules move within the cell or from one cell to another through different strategies. Transport may be in the form of..
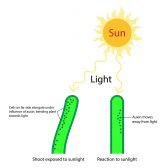
Plant Auxins – Phototropism & Geotropism
Plants produce hormones to regulate their growth. Auxins, for instance, influence plant growth. Know the role of auxin i..

Vascular Plants: Ferns and Relatives
Ferns and their relatives are vascular plants, meaning they have xylem and phloem tissues. Because of the presence of va..

Ecosystem Succession
If the balance of nature is left untouched, landscapes can change dramatically over time. A previous ecosystem is supers..

Animal Water Regulation
Animals adapt to their environment in aspects of anatomy, physiology, and behavior. This tutorial will help you understa..

Plant Cells vs. Animal Cells
Plant cells have plastids essential in photosynthesis. They also have an additional layer called cell wall on their cell..

