siphon
1. A device, consisting of a pipe or tube bent so as to form two branches or legs of unequal length, by which a liquid can be transferred to a lower level, as from one vessel to another, over an intermediate elevation, by the action of the pressure of the atmosphere in forcing the liquid up the shorter branch of the pipe immersed in it, while the continued excess of weight of the liquid in the longer branch (when once filled) causes a continuous flow. The flow takes place only when the discharging extremity of the pipe ia lower than the higher liquid surface, and when no part of the pipe is higher above the surface than the same liquid will rise by atmospheric pressure; that is, about 33 feet for water, and 30 inches for mercury, near the sea level.
2. (Science: zoology) One of the tubes or folds of the mantle border of a bivalve or gastropod mollusk by which water is conducted into the gill cavity. The anterior prolongation of the margin of any gastropod shell for the protection of the soft siphon.
The tubular organ through which water is ejected from the gill cavity of a cephaloid. It serves as a locomotive organ, by guiding and confining the jet of water. Called also siphuncle.
The siphuncle of a cephalop
ba7
od shell.
The sucking proboscis of certain parasitic insects and crustaceans.
A sproutlike prolongation in front of the mouth of many gephyreans.
A tubular organ connected both with the oesophagus and the intestine of certain sea urchins and annelids.
3. A siphon bottle.
(Science: physics) inverted siphon, a tube bent like a siphon, but having the branches turned upward; specifically, an oil cup in which oil is carried over the edge of a tube in a cotton wick, and so reaches the surface to be lubricated. Siphon gauge. See Gauge. Siphon pump, a jet pump. See Jet.
Origin: F. Siphon, L. Sipho, -onis, fr. Gr. A siphon, tube, pipe.
(Science: chemistry) To convey, or draw off, by means of a siphon, as a liquid from one vessel to another at a lower level.
Dictionary > Siphon
You will also like...

The Dinosaurs
Dinosaurs represented a major turn in the evolutionary development of organisms on Earth. The first dinosaurs were presu..

Geological Periods
Geological periods is a study guide that cites the different geological periods on Earth's timeline. Each has a brief ov..

Lotic Communities & Animals
A running water environment offers numerous microhabitats for many types of animals. Similar to plants, animals in lotic..

Homeostatic Mechanisms and Cellular Communication
Homeostasis is the relatively stable conditions of the internal environment that result from compensatory regulatory res..

Role of Golgi Apparatus & Endoplasmic Reticulum in Protein Synthesis
The endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus are the organelles involved in the translation step of protein synthesis a..
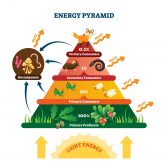
Freshwater Community Energy Relationships – Producers & Consumers
This tutorial looks at the relationship between organisms. It also explores how energy is passed on in the food chain an..

