unified atomic mass unit
n., plural: unified atomic mass units
/juːˌnɪfaɪd əˈtɒmɪk mæs ˌjuː.nɪt/
Definition: A standardized measure of atomic and molecular mass
Table of Contents
Unified Atomic Mass Unit Definition
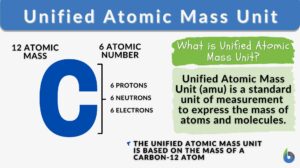
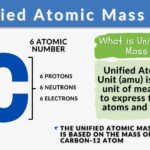
The Unified Atomic Mass Unit (u) (or simply atomic mass unit) refers to the 1/12 (0.0833) mass of the carbon-12 atom. It is used to express the mass of atomic and subatomic particles. It is predominantly used in chemistry and physics as a fundamental unit of measurement that quantifies the mass of atoms and molecules on the atomic scale.
This unit is crucial for precise and consistent measurements of atomic and molecular masses that help scientists bridge the gap between the microscopic aspect of atomic nuclei and the macroscopic feature of chemical compounds.
Etymology: The term “unified atomic mass unit” originates from the unification of various atomic mass scales and the use of this unit to express atomic masses consistently.
Variant: Atomic Mass Unit
Abbreviation: amu; u
Understanding Atomic Mass Units (by Professor Dave Explains):
NOTE IT!
The unified atomic mass unit is approximately equal to 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 atom. So, the value of one unified atomic mass unit is equal to 1 amu, determined by dividing the mass of a carbon-12 atom (which is 12) by 12, i.e., 12 amu (of 12C )/ 12 = 1. This makes carbon-12 a crucial reference isotope.
Historical Development And Standardization
The Unified Atomic Mass Unit’s origin can be dated back to the time when scientists needed a consistent and unified unit for measuring atomic masses as various atomic mass scales had been used resulting in confusion and inconsistencies in scientific research. Thus, the concept of a unified unit came about to address this issue. At this time, the atomic mass unit is based on the carbon-12 atom.
Below is a brief timeline of its historical development:
- Atomic Mass Unit is also called dalton, named after John Dalton, who proposed in 1803 to use the mass of hydrogen atoms as the natural unit for relative atomic mass.
- The hydrogen was replaced later on with oxygen atom. Wilhelm Ostwald suggested basing the relative atomic mass in terms of 1/16 mass of oxygen in 1903. Thus, formerly, the atomic mass unit is based on natural oxygen.
- Years later (in 1929), isotopic oxygen was discovered and as such it resulted in the divergence in relative atomic mass representation. The divergence could result in errors.
- To prevent this carbon-12 was eventually used as the reference standard in 1961.
Applications
Atomic Mass Unit (amu) facilitates accurate measurements and comparisons in the fields of pure and applied physics and chemistry, and other related scientific disciplines, including biology.
Atomic and nuclear physics
It helps understand the fundamental components of matter, such as protons, neutrons, and electrons, as well as the more advanced nuclear physics contexts, such as understanding the unbound atoms and the binding energy that holds them together inside the atomic nuclei.
Pure and applied chemistry
This unit allows chemists to determine the masses of individual atoms and molecules, aiding in stoichiometry, reaction kinetics, and the study of chemical compounds. Additionally, it simplifies mass calculations for molecules and serves as the foundation for calculating molar masses in the natural unit, thus facilitating the formulation and analysis of chemical compounds. This unit is closely associated with the atomic mass constant, ensuring that atomic weights and average masses can be consistently measured.
Biology
The atomic mass unit is useful, particularly in the fields of biochemistry and molecular biology, as it is used as a tool for understanding the composition and behavior of biomolecules, including proteins, nucleic acids, and carbohydrates. Researchers use it to measure the molecular mass of biological molecules, including the determination of the composition of DNA and proteins. This is crucial especially when wanting to determine the stoichiometry of biochemical reactions, structure, and function. This unit can also be applied in calculating the average molecular mass with precision. As molecular mass calculations are based on this unit, the masses of individual atoms can be added together to determine the total mass of a molecule.
This concept of Unified Atomic Mass Units facilitates the consistent representation of relative atomic mass and molecular mass, providing a common measurement framework in the study of atomic and molecular structures across various related disciplines.
The carbon-12 isotope that has a mass of exactly 12 u makes it useful in standardizing measurements. Scientists and researchers can use this same unit when quantifying the masses of various elements and compounds.
Calculating the molecular mass of a chemical compound or a biomolecule, for instance, involves adding up the masses of its constituent atoms, each measured in u, which in so doing can help determine the total mass of the compound.
This is particularly useful for various applications, including the preparation of chemical solutions, drug design, and understanding the molecular basis of biological processes.
NOTE IT!
The concept of the Unified Atomic Mass Unit was introduced to unify various atomic mass scales and promote consistency in empirical measurements. Whether measuring the mass of a single atom or employing mass spectrometry to analyze complex compounds, the Unified Atomic Mass Unit is a fundamental tool for precise and universally accepted mass measurements in multifarious scientific research.
Sample Calculation
Question: Calculate the molecular mass of a water molecule (H2O) involving amu
Answer: Molecular mass of a water molecule (H2O) = 18.015 amu
Solution:
First, let us identify the given atomic masses of the atoms that comprise a water molecule in amu, which can be found in the Periodic Table of the Elements below:
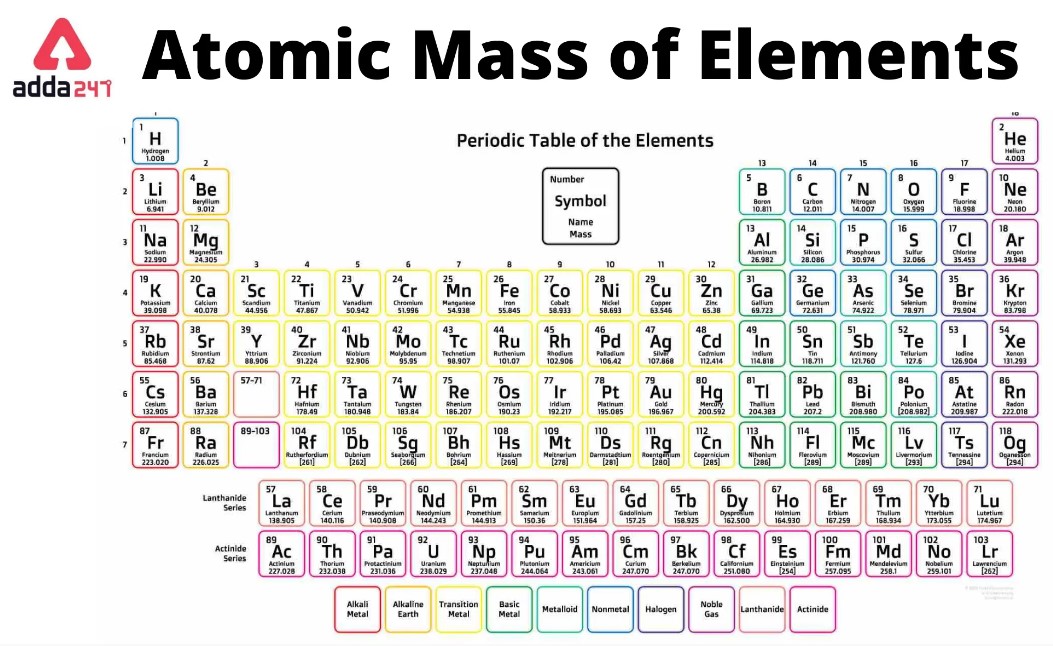
- Hydrogen: The atomic mass of hydrogen (H) is approximately 1.008 amu.
- Oxygen: The atomic mass of oxygen (O) is approximately 15.999 amu.
Second, add up the atomic masses in the water molecule, H2O:
- Molecular mass = (2 × Atomic mass of hydrogen) + (1 × Atomic mass of oxygen)
- Molecular mass = (2 × 1.008 amu) + (1 × 15.999 amu)
- Molecular mass = 2.016 amu + 15.999 amu
- Molecular mass of a water molecule (H2O) = 18.015 amu
What does this imply?
The molecular mass of a water molecule is approximately 18.015 amu. This means the total mass of a water molecule is about 18 times the mass of the standard unified atomic mass unit.
Further Reading
References
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). (2021). Unified atomic mass unit. https://physics.nist.gov/cuu/Constants/
- Berg, J. M., Tymoczko, J. L., & Gatto Jr, G. J. (2019). Biochemistry. W. H. Freeman.
- Lodish, H., Berk, A., Kaiser, C. A., Krieger, M., Scott, M. P., Bretscher, A., & Ploegh, H. (2016). Molecular Cell Biology. W. H. Freeman.
©BiologyOnline.com. Content provided and moderated by Biology Online Editors.