Search Results for: acid
Pyruvic acid
What is Pyruvic Acid? Pyruvic acid is an organic acid that occurs as an intermediate in many metabolic processes. It occurs... Read More
Nucleic acid
Nucleic Acid Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds consisting of chains of monomers of... Read More
Fatty acid
Definition noun plural: fatty acids'' fatty acid, ˈfætɪ ˈæsɪd Any of the group of a long chain of hydrocarbon... Read More
Ribonucleic acid
Ribonucleic Acid Definition noun (uncountable), ribonucleic acids ri·bo·nu·cle·ic ac·id, raɪboʊnjuːkliːɪk... Read More
Unsaturated fatty acid
Definition noun, plural: unsaturated fatty acids The unsaturated fatty acid is a form of fatty acid containing one or more... Read More
Monounsaturated fatty acid
Definition noun, plural: monounsaturated fatty acids Any of a group of unsaturated fatty acids characterized by having a... Read More
Transfer ribonucleic acid
Definition noun plural: transfer ribonucleic acids trans•fer ri•bo•nu•cle•ic ac•id, ˈtɹænsfɝ... Read More
Deoxyribonucleic acid
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds made up of linear... Read More
Saturated fatty acid
Definition noun, plural: saturated fatty acids A form of fatty acid with only single bonds between carbon atoms Supplement A... Read More
Polyunsaturated fatty acid
Definition noun, plural: polyunsaturated fatty acids Any of a group of unsaturated fatty acids characterized by having more... Read More
Stearic acid
Definition noun, plural: stearic acids A eighteen-carbon fatty acid, with the formula: C18H36O2 Supplement A fatty acid is a... Read More
Omega-6 fatty acid
Definition noun, plural: omega-6 fatty acids A type of polyunsaturated fatty acid in which the first double bond is between... Read More
Palmitic acid
Definition noun, plural: palmitic acids A 16-carbon fatty acid, with the formula: CH3 (CH2)14 COOH Supplement A fatty acid... Read More
Amino acid
Definition noun, plural: amino acids (1) A molecule consisting of the basic amino group (NH2), the acidic carboxylic group... Read More
Malic acid
Definition noun A dicarboxylic acid produced by a living organism, with a chemical formula: C4H6O5 Supplement Malic acid is... Read More
Lactic acid
Definition noun (1) A colorless or yellowish, syrupy, water-soluble liquid, which is a byproduct of anaerobic glucose... Read More
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid
Definition noun plural: ribosomal ribonucleic acids ri•bo•so•mal ri•bo•nu•cle•ic ac•id, ˈraɪ... Read More
Gastric acid
Definition noun (1) The hydrochloric acid present in the gastric juice (2) The gastric juice itself Supplement The gastric... Read More
Cis fatty acid
Definition noun, plural: cis fatty acids A fatty acid in a cis configuration, i.e. two hydrogen atoms adjacent to the double... Read More
Messenger ribonucleic acid
Definition noun plural: messenger ribonucleic acids mes•sen•ger ri•bo•nu•cle•ic ac•id, ˈmɛ.sɪn.dʒəɹ... Read More
Fermentation
Fermentation Definition What is fermentation? Fermentation is the breaking down of sugar molecules into simpler compounds... Read More
Hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid (Science: chemical) hydrochloric acid. Solutions of hydrogen chloride gas in water. It is a highly... Read More
Frameshift mutation
Define Frameshift Mutation What is a frameshift mutation? In biology, insertions or deletions of nucleotides in the coding... Read More
Anaerobic respiration
Anaerobic Respiration Definition What is anaerobic respiration? Anaerobic (cellular) respiration is a respiratory process... Read More
Hyaluronic acid
Definition noun A linear mucopolysaccharide that is a major component of tissues, such as connective, epithelial and neural... Read More
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that... Read More
Silent mutation
A mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene or a chromosome. When there is only one nucleotide involved, it... Read More
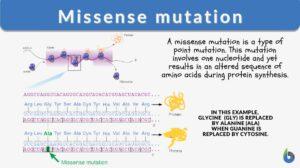
Missense mutation
What is a missense mutation? Literally speaking, a mutation that changes the meaning of the encoded gene sequence is the... Read More
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
Dibasic amino acid
Dibasic amino acid --> basic amino acid An amino acid containing a second basic group (usually an amino group); e.g.,... Read More
Citric Acid Cycle
Definition noun (1) A cycle of reactions catalyzed by enzymes in which pyruvate derived from nutrients and converted to... Read More