Search Results for: agent
Reservoir host
Reservoir Host Definition A reservoir host is a host that harbors the pathogen and serves as a source of the infective... Read More
Cardiotonic agent
Cardiotonic agent agents that have a tonic effect on the heart or increase cardiac output. They may be glycosidic steroids... Read More
Susceptible
Resistance, vulnerability, sensitivity, tolerance, and susceptibility are some highly important terminologies across the... Read More
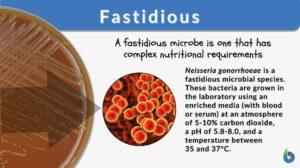
Fastidious
Fastidious Definition We can define fastidious as a term used in microbiology to denote a species that lacks the ability to... Read More
Hydrophilic
Hydrophilic Definition What does a hydrophile (or hydrophilic molecule) mean? If a molecule is “water-loving”, it is... Read More
Chelating agent
Definition noun, plural: chelating agents A ligand, often an organic compound, which reacts with a metal ion to produce a... Read More
Parthenogenesis
To reproduce, by definition, means to produce new offspring. The process is referred to as reproduction, which is one of the... Read More
Reducing sugar
Reducing Sugar Definition What is reducing sugar? The type of sugar that acts as the reducing agent and can effectively... Read More
Flavin mononucleotide
Definition noun plural: flavin mononucleotides fla·vin mon·o·nu·cle·o·tide, ˌmɒnəʊˈnjuːklɪəˌtaɪd A... Read More
Ferrous lactate
Definition noun A greenish white crystal or (powder) made up of iron (Fe2+) and lactate anions Supplement Ferrous lactate is... Read More
Redox reaction
Redox Reaction Definition What are redox reactions? This is a common term in chemistry and biology. In chemistry, a redox... Read More
Disinfectant
Disinfectant An agent that disinfects, applied particularly to agents used on inanimate objects. Compare: antiseptic. An... Read More
Lactic acid
Definition noun (1) A colorless or yellowish, syrupy, water-soluble liquid, which is a byproduct of anaerobic glucose... Read More
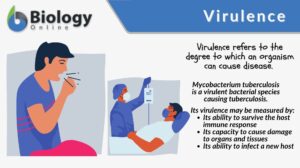
Pathogenicity
Definition noun, plural: pathogenicities The capability (of a pathogenic agent) to cause disease Supplement Pathogenicity... Read More
Communicable disease
Definition noun, plural: communicable diseases A type of disease that is contagious since the agent of the disease may be... Read More
Electron acceptor
Definition noun A molecule that receives or accepts electrons from another molecule during a redox reaction. Supplement An... Read More
Yellow fever virus
Definition noun, plural: yellow fever viruses A Flavivirus species containing positive-sense, single-stranded RNA with about... Read More
Plant Cell Defense
Hydrogen Peroxide Plants release hydrogen peroxide in response to the presence of a fungal invasion, which attacks by... Read More
Haemostatic
Definition adjective (1) Capable of stopping haemorrhage or bleeding. (2) An agent or device that can arrest haemorrhage or... Read More
Methyl aldehyde
methyl aldehyde --> formaldehyde (Science: chemical) Commonly used fixative and antibacterial agent. As a fixative it is... Read More
Diaphoresis
What is Diaphoresis? Diaphoresis is referred to excessive or profuse perspiration or sweating which may be due to... Read More
Demecolcine
Definition noun (cytogenetics) A cytotoxic alkaloid isolated from Colchicum autumnale, and is used as an antineoplast... Read More
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
Definition noun A coenzyme made up of ribosylnicotinamide 5'-phosphate (nmn) coupled by pyrophosphatelinkage to the... Read More
Opportunistic pathogen
Opportunistic Pathogen Definition How do we define opportunistic pathogen? The opportunistic pathogen is an infectious... Read More
Disaccharide
Carbohydrates are organic compounds comprised of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, usually in the ratio of 1:2:1. They are one... Read More
Facultative anaerobe
Facultative Anaerobe Definition What does facultative anaerobe mean? Facultative organisms are the most adaptable... Read More
Fluctuation test
Fluctuation test (Science: investigation) test devised by Luria and Delbruck to determine whether genetic variation in a... Read More