Search Results for: arm
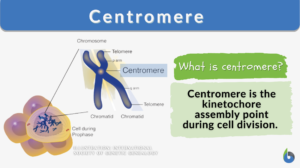
Centromere
Centromere Definition Centromere is defined as the point of attachment for the sister chromatids generated after DNA... Read More
Upper lateral cutaneous nerve of arm
upper lateral cutaneous nerve of arm --> superior lateral brachial cutaneous nerve (Science: anatomy, nerve) The terminal... Read More
Chromosome
Chromosomes Definition Chromosomes are thread-like structures present in the nucleus of plant and animal cells. Chromosomes... Read More
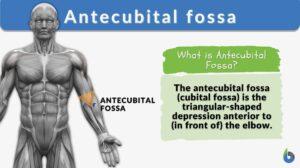
Antecubital fossa
Antecubital Fossa Definition The antecubital fossa or the cubital fossa is the triangular-shaped hollow depression between... Read More
Chromatids
Chromatid Definition Chromatids are found inside our cells. Chromatids are condensed chromosomes distinguishable during... Read More
Muscular system
Muscular System Definition What is the muscular system? The muscular system is a system that includes muscle cells and... Read More
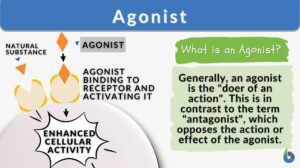
Antagonistic Muscle
Definition of Antagonistic Muscle What does the term “antagonistic” mean? As the name suggests, the word antagonistic... Read More
Transfer ribonucleic acid
Definition noun plural: transfer ribonucleic acids trans•fer ri•bo•nu•cle•ic ac•id, ˈtɹænsfɝ... Read More
Antebrachium
Definition noun, plural: antebrachia The forearm, i.e. the part of the arm between the elbow and the wrist. Supplement The... Read More
Paracentric inversion
Definition noun, plural: paracentric inversions (genetics) An inversion of a segment of chromosome in which the centromere... Read More
Regeneration in humans – Finding the gene switch
Regeneration in humans is much more limited compared in other animals. Say for instance when one lost a limb, much as well... Read More
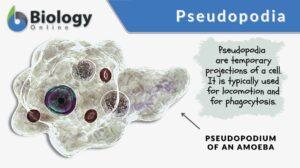
Pseudopodia
A pseudopodium (plural: pseudopodia) refers to the temporary projection of the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell. Pseudopodia... Read More
Constitutive heterochromatin banding
Definition noun (cytogenetics) A selective banding technique wherein a banding pattern is produced in the constitutive... Read More
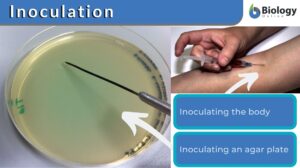
Inoculation
Inoculation Definition In Immunology, inoculation is defined as the process of introducing an antigenic substance or... Read More
Chromosomal inversion
Definition noun, plural: chromosomal inversions A chromosomal aberration wherein a segment of a chromosome is reversed... Read More
Haemophilia A
Definition noun A form of haemophilia that is caused by a deficiency in blood clotting factor VIII due to a gene defect in... Read More
Metacentric chromosome
Definition noun, plural: metacentric chromosomes A chromosome in which the centromere is located in the middle resulting in... Read More
Pericentric inversion
Definition noun, plural: pericentric inversions (genetics) An inversion of a segment of chromosome in which the centromere... Read More
Subtelocentric chromosome
Definition noun, plural: subtelocentric chromosomes A chromosome whose centromere is placed near the end rather than the... Read More
Protein synthesis
Protein synthesis is the process of creating protein molecules. In biological systems, it involves amino acid synthesis,... Read More
Telocentric chromosome
Definition noun, plural: telocentric chromosomes A chromosome whose centromere is placed very close to the end of the... Read More
Proprioception
Definition noun A sensory perception of motion and relative position of the body through the receptors in tissues such as... Read More
Genetic locus
Definition noun, plural: genetic loci The location of a gene (or of a significant sequence) on a chromosome or on a linkage... Read More
Chelicerate
Definition noun, plural: chelicerates Any of the species belonging to the subphylum Chelicerata Supplement The chelicerates... Read More
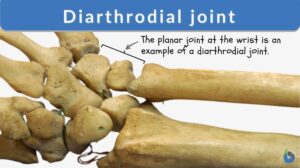
Diarthrodial joint
What is a diarthrodial joint? A diarthrosis joint is a freely moving joint characterized by its mobility and joint cavity... Read More
Skeletal system
What is the Skeletal System? How to define a skeleton? The skeletal system is the main framework that gives your body its... Read More
Dawbarns sign
Dawbarns sign (Science: clinical sign) pain of subacromial bursitis disappears when the arm is... Read More
Proprioceptor
Definition noun, plural: proprioceptors A sensory receptor located in the subcutaneous tissues, and is capable of detecting... Read More
Centromeric index
Centromeric index The ratio of the length of the short arm of the chromosome to that of the total chromosome; ordinarily... Read More