Search Results for: cancer
RASER proteins selectively “hack” and “shut down” cancer cells
According to World Health Organization, cancer is the second leading cause of death worldwide. The record showed that it... Read More
Autocrine signaling
Autocrine Signaling Definition What is autocrine signaling? Autocrine signaling is a type of cell signaling wherein a cell... Read More
Predisposing factors
All organisms can be born with or develop a disease at any point in their lifetime. When someone is born with a disease, it... Read More
Cell adhesion
Cell Adhesion Definition Cell adhesion is the process in which a cell uses a specialized complex of proteins to get... Read More
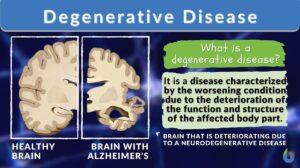
Degenerative disease
Degenerative Disease Definition A degenerative disease is defined as a disease characterized by the worsening condition due... Read More
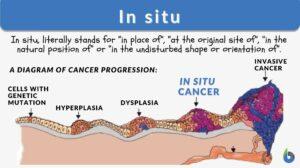
Spider cancer
Definition noun A term no longer in common use to refer to a malignant neoplasm having a rhizoid or filamentous edge of... Read More
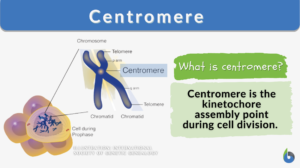
Centromere
Centromere Definition Centromere is defined as the point of attachment for the sister chromatids generated after DNA... Read More
Cells know when to separate at mitosis
How do cells know when to separate during mitosis? A molecule called BubR1 was found to regulate the timing of the division... Read More
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
Genetic Information and Protein Synthesis
Genetic Code Genes are sequences of DNA nucleotides that carry and transmit the information specifying amino acid sequences... Read More
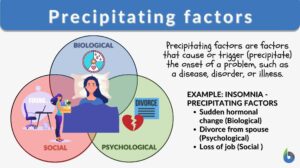
Precipitating factors
Precipitating Factor Definition Precipitating factors are factors that initiate or promote the onset of any illness,... Read More
Skeletal system
What is the Skeletal System? How to define a skeleton? The skeletal system is the main framework that gives your body its... Read More
Frameshift mutation
Define Frameshift Mutation What is a frameshift mutation? In biology, insertions or deletions of nucleotides in the coding... Read More
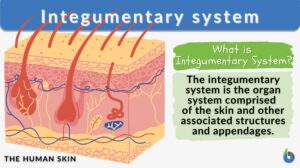
Integumentary system
Integumentary System Definition The integumentary system is the outermost layer of the body. The animal body, in... Read More
Diaphoresis
What is Diaphoresis? Diaphoresis is referred to excessive or profuse perspiration or sweating which may be due to... Read More
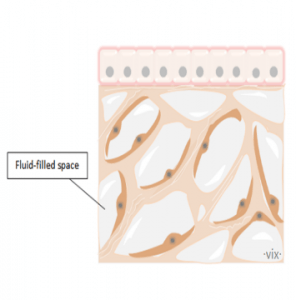
The interstitium – a new biological organ?
Scientists found, apparently by accident, a new biological organ and they want it called "interstitium". The discovery was... Read More
Centrosome
Centrosome Definition What is a centrosome? The centrosome is considered to be the main microtubule-organizing... Read More
Y chromosome
Y chromosome Definition The Y chromosome constitutes one member of the pair of sex chromosomes within an organism, a common... Read More
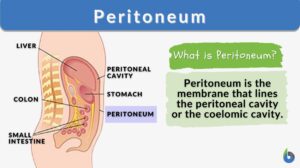
Peritoneum
What is the Peritoneum? The term peritoneum refers to the serous membrane that constitutes the biologically active inner... Read More
Lymph nodes
Lymph nodes definition Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped organs located in different parts of the body and act as... Read More
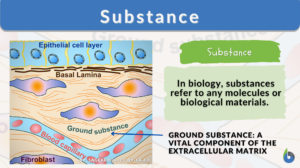
Fibroblast
The building block of living things is known as the cell. The cell contributes to many parts and functions of different... Read More
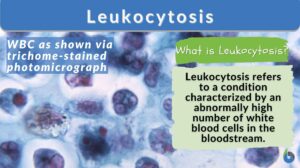
Leukocytosis
What Is Leukocytosis? Leukocytosis is a condition wherein the number of White Blood Cells (WBCs) is increased above the... Read More
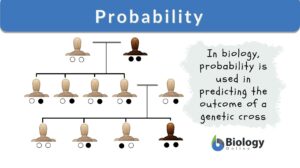
Probability
Probability DefinitionHow do you define probability? In science, probability is a measurement tool that calculates the... Read More
Tight junction
What are tight junctions? Tight junctions are the intercellular barrier between two neighboring endothelial and epithelial... Read More
Proteoglycan
What are proteoglycans? Proteoglycans are primarily a type of polysaccharide. Structurally, proteoglycans are... Read More
Redox reaction
Redox Reaction Definition What are redox reactions? This is a common term in chemistry and biology. In chemistry, a redox... Read More