Search Results for: capillaries
Capillaries
Capillaries (Science: anatomy) The smallest vessels which contain oxygenated blood. The capillaries, allowing red blood... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More
Lymph capillary
Definition noun, plural: lymphatic capillaries (anatomy) A minute, thin-walled vessel of the lymphatic system that is... Read More
Kidneys and Regulation of Water and Inorganic Ions
Renal Functions Kidneys remove/add substances from/to the plasma.Regulate water concentration, inorganic ion... Read More
Osmotic pressure
Osmotic Pressure Definition Osmotic pressure is the pressure caused by a difference in the amounts of solutes (or... Read More
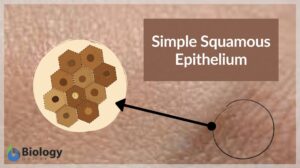
Simple squamous epithelium
Simple Squamous Epithelium Definition Simple squamous epithelium, also known as simple squamous epithelial tissue or... Read More
Respiration
Organization of the Respiratory System Each lung is composed of air sacs called alveoli - the sites of gas exchange with... Read More
Single cycle circulation
Definition noun A type of blood circulation in which the system has only one circuit, with the blood being pumped through... Read More
Glycocalyx
What is the Glycocalyx? The glycocalyx is a polysaccharide-based gel-like, highly hydrous cellular thin layer, covering... Read More
Lymphatic vessel
Definition noun, plural: lymphatic vessels (anatomy) A vessel that carries lymph and is responsible for the removal of... Read More
Blood vessel
Definition noun, plural: blood vessels Any of the vessels in cardiovascular system and functions by carrying blood... Read More
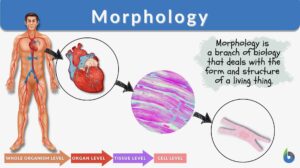
Morphology
Morphology Definition Morphology means the study of the shape and structure of living things from a biological perspective.... Read More
Erythrocyte
Erythrocyte Definition Erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs) are the myeloid series of specialized cells that play an... Read More
Pulmonary venule
Definition noun, plural: pulmonary venules The venule surrounding the alveolus of the lung and carries oxygen-rich... Read More
Cardiovascular system
Definition noun The organ system in which the blood is pumped through the heart and circulates throughout the body through... Read More
Closed circulatory system
Definition noun A type of circulatory system where blood circulates within closed vessels, thus, blood is distinct from... Read More
Schistosoma
Definition noun (taxonomy) A genus of the Phylum Platyhelminthes that is comprised of parasitic... Read More
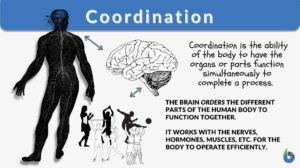
Coordination
Coordination Definition When a person hears the word coordination, they think of order, organization, or even managing... Read More
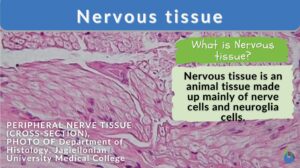
Nervous tissue
Nervous Tissue Definition Nerve cells (or neurons) and their associated cells, such as neuroglia cells, make up nervous... Read More
Plasma membrane
Do all cells have a plasma (or cell) membrane? Yes, all cells have a biological membrane that separates the protoplasm from... Read More
Muscular system
Muscular System Definition What is the muscular system? The muscular system is a system that includes muscle cells and... Read More
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis Definition Phagocytosis is a basic physiological cellular process wherein a cell ingests a solid particle... Read More
Regulation of Organic Metabolism, Growth and Energy Balance
Organic Metabolism Events of Absorptive and Post-absorptive States. The absorptive state is the period during which... Read More
Glomerulus
A small intertwined group of capillaries in the malpighian body; glomeruli filter blood during urine formation.A closely... Read More
Fahraeus-lindqvist effect
Fahraeus-lindqvist effect The decrease in apparent viscosity that occurs when a suspension, such as blood, is made to flow... Read More
Carbohydrate
Carbohydrate Definition A biomolecule refers to any molecule that is produced by living organisms. As such, most of them... Read More
Polysaccharide
Polysaccharide Definition Biology Definition: A polysaccharide is a carbohydrate formed by long chains of repeating units... Read More
Anastomosis
Definition noun, plural: anastomoses (1) Interconnection between parts of a branching system forming a network, as in leaf... Read More
Brown adipose tissue
Definition noun, plural: brown adipose tissues A type of adipose tissue found in mammals that is brownish as opposed to... Read More
Systemic venule
Definition noun, plural: systemic venules The venule that connects the capillary bed to the systemic vein to return the... Read More



![Osmotic pressure n., plural: osmotic pressures [ɑsˈmɑtɪk ˈpɹɛʃ.ɚ] osmotic pressure definition and example](https://www.biologyonline.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/osmotic-pressure-definition-and-example-300x168.jpg)