Search Results for: carrier
Carrier protein
Carrier protein is a type of cell membrane protein involved in facilitated diffusion and active transport of substances out... Read More
Incubatory carrier
Incubatory carrier An individual capable of transmitting an infectious agent to others during the incubation period of the... Read More
Ion carrier
Definition noun, plural: ion carriers An ionophore that facilitates transport of ion through a hydrophobic medium, such as... Read More
Carrier state
Carrier state a condition in which a human who is not himself sick harbors an infective organism which may cause disease in... Read More
Sex-linked trait
Definition of Sex-Linked Traits A sex-linked trait is an observable characteristic of an organism that is influenced by the... Read More
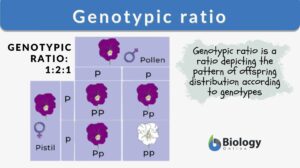
Genotypic ratio
Genotypic Ratio Definition To understand 'Genotypic ratio', let us first understand the terms: 'Genotype' and 'Phenotype'.... Read More
Facilitated diffusion
Facilitated diffusion is the transport of substances across a biological membrane from an area of higher concentration to an... Read More
Electron carriers
Definition noun, plural: electron carriers A molecule capable of accepting one (or more than one) electrons from another... Read More
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that... Read More
Light-dependent reaction
Many organisms, such as green plants, convert light energy into chemical energy through the mechanism of photosynthesis. In... Read More
Steroid hormone
Definition noun, plural: steroid hormones A type of steroid that acts as a hormone, and that which is exemplified by sex... Read More
Reverse passive agglutination
Definition noun A type of agglutination reaction in which known antibody is bound to a carrier particle instead of the... Read More
Permanent Tattoo Means Permanent Immune Action Of Macrophages
Have you ever wondered why a permanent tattoo seemed to last forever? A simple assumption would be is that the ink could... Read More
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
Definition noun A coenzyme made up of ribosylnicotinamide 5'-phosphate (nmn) coupled by pyrophosphatelinkage to the... Read More
Biological Cell Introduction
It only takes one biological cell to create an organism. In fact, there are countless species of single-celled organisms,... Read More
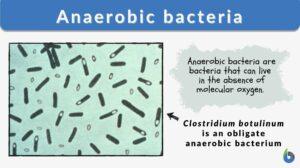
Anaerobic bacteria
Bacteria are classified according to the need for oxygen to survive and grow. For example, aerobic bacteria are bacteria... Read More
Reservoir host
Reservoir Host Definition A reservoir host is a host that harbors the pathogen and serves as a source of the infective... Read More
Inbreeding
Inbreeding is a type of breeding or mating where closely related individuals with a common ancestor produce progenies with... Read More
Selectively-permeable membrane
Selectively Permeable Membrane Definition We can define selectively permeable membranes as those that are selectively... Read More
Plant Metabolism
Introduction Plants are responsible for incredible feats of molecular transformation. The processes are always being... Read More
X-linked inheritance
Definition noun (genetics) Inheritance for genes on the X chromosome Supplement Sex chromosomes are not only relevant for... Read More
Cell Respiration
As mentioned in the previous tutorial on ATP, the process of respiration is split into 3 distinct areas that occur at... Read More
Calvin cycle
Calvin Cycle Definition The Calvin cycle, also known as the Calvin Benson cycle or the dark reactions, is a series of... Read More
Nuclear envelope
Definition noun plural: nuclear envelopes nu·cle·ar en·ve·lope, ˈn(j)ukliɚ ˈɛn.və.ləʊp The two layered membrane... Read More