Search Results for: contraction
Antagonistic Muscle
Definition of Antagonistic Muscle What does the term “antagonistic” mean? As the name suggests, the word antagonistic... Read More
Idiomuscular contraction
Idiomuscular contraction --> myoedema a localised contraction of a degenerating muscle, occurring at the point of a sharp... Read More
Muscular system
Muscular System Definition What is the muscular system? The muscular system is a system that includes muscle cells and... Read More
Tonic contraction
tonic contraction Sustained contraction of a muscle, as employed in the maintenance of... Read More
Anodal opening contraction
Anodal opening contraction An obsolete term for the momentary contraction of a muscle under the influence of the positive... Read More
Muscle contraction
muscle contraction A process leading to shortening and/or development of tension in muscle tissue. Muscle contraction occurs... Read More
Contraction
Contraction (Science: physiology) a shortening or reduction in size, in connection with muscles contraction implies... Read More
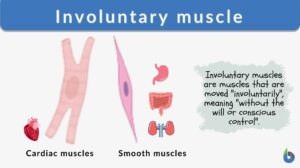
Involuntary muscle
A muscle act typically either under the control of the will or without conscious control. Muscles that can be controlled at... Read More
Sarcolemma
Sarcolemma Definition What is the sarcolemma? It is the thin, transparent, extensible plasma membrane of the muscle cell.... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
Smooth muscle
The smooth muscle can be described as a type of muscle in the human body that is non-striated and involuntary in action.... Read More
Myocardium
Myocardium Definition What is the myocardium of the heart? It is the muscular middle layer of the heart that is... Read More
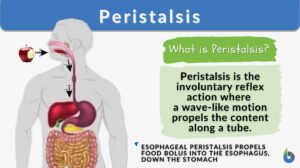
Peristalsis
What is Peristalsis? Peristalsis is the series of involuntary, wave-like muscle movements in the cylindrical, hollow tube... Read More
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the tendency not to stray from the range of favorable or ideal internal conditions. Such conditions must be... Read More
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (sER) is part of or a region in the endoplasmic... Read More
Cytokinesis
The cell cycle of eukaryotes is a cyclical series of biological events that certain asexual cells go through. The cell cycle... Read More
Positive feedback
Positive Feedback Definition Each mechanism of the body like temperature, blood pressure, and levels of specific nutrients... Read More
Regulation of Organic Metabolism, Growth and Energy Balance
Organic Metabolism Events of Absorptive and Post-absorptive States. The absorptive state is the period during which... Read More
Digestion and Absorption of Food
The gastrointestinal (GI) system includes the gastrointestinal tract (mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,... Read More
Abdominal reflex
Definition noun, plural: abdominal reflexes Abdominal wall muscle contraction of the umbilicus toward the abdominal quadrant... Read More
Cytoskeleton
Definition noun plural: cytoskeletons cy·to·skel·e·ton (cell biology) The lattice or internal framework of a cell... Read More
Starlings law
Definition noun Starling’s law states that the force of contraction depends on the length of muscle fibers of the heart... Read More
Prostaglandin
Definition noun, plural: prostaglandins A group of eicosanoids, structurally characterized as 20-carbon unsaturated fatty... Read More
Terminal web
Definition noun (cell biology) The subapical zone rich in microfilaments, and acts as the attachment point for the bundles... Read More
Prostaglandin F2-alpha
Definition noun, plural: prostaglandins F A biologically active prostaglandin that forms when the intermediate prostaglandin... Read More
Microfilament
Definition noun plural: microfilaments mi·cro·fil·a·ments, mī'krō-fil'ă-mĕnts A thin, helical, single-stranded... Read More
Stroke volume
stroke volume (Science: physiology) The amount of blood pumped out of one ventricle of the heart as the result of a single... Read More
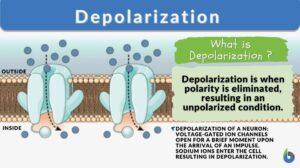
Depolarization
Depolarization is the removal of polarity by a process or action. It might also be used to describe how such activity leads... Read More
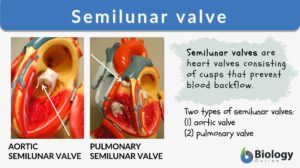
Semilunar valve
The human heart structure consists of heart chambers (2 atria and 2 ventricles) that differ functionally from each other.... Read More