Search Results for: coupling
Energy coupling
What is Energy Coupling? Work, whether it be physical or biological, requires energy to be expended. In biological... Read More
Coupling phase
Coupling phase The physical relationship of two syntenic genes. If they are on the same chromosome, they are said to be in... Read More
Chemiosmotic coupling hypothesis
Definition noun A theory postulated by the biochemist Peter Mitchell in 1961 to describe ATP synthesis by way of a proton... Read More
Sarcolemma
Sarcolemma Definition What is the sarcolemma? It is the thin, transparent, extensible plasma membrane of the muscle cell.... Read More
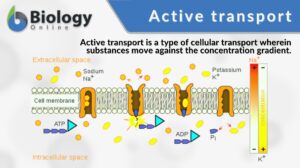
Active transport
Active transport is a type of cellular transport in which substances (e.g. ions, glucose, and amino acids) are transported... Read More
Chemiosmosis
Chemiosmosis Definition What is chemiosmosis? In biology, chemiosmosis refers to the process of moving ions (e.g. protons)... Read More
Plant Metabolism
Introduction Plants are responsible for incredible feats of molecular transformation. The processes are always being... Read More
Chemiosmotic coupling
Definition noun The process that couples or links the electron transport chain to ATP synthesis. Supplement Chemiosmosis is... Read More
Chemiosmotic theory
Definition noun A theory postulated by the biochemist Peter Mitchell in 1961 to describe ATP synthesis by way of a proton... Read More
Carrier protein
Carrier protein is a type of cell membrane protein involved in facilitated diffusion and active transport of substances out... Read More
Mitochondrion
Mitochondrion Definition What are mitochondria? The term “mitochondrion” comes from the two words of the Greek... Read More
On Mate Selection Evolution: Are intelligent males more attractive?
A study published in Science on January 11 seems to be the first to lay empirical evidence that concur with Charles Darwin's... Read More
Chemiosmotic hypothesis
Definition noun A theory postulated by the biochemist Peter Mitchell in 1961 to describe ATP synthesis by way of a proton... Read More
Carbohydrate
Carbohydrate Definition A biomolecule refers to any molecule that is produced by living organisms. As such, most of them... Read More
Nucleosome
Nucleosome Definition Every organism is made of deoxyribonucleic acid, also known as DNA. DNA is made up of numerous... Read More
Disulfide bond
Definition noun (chemistry) (1) The single covalent bond formed from the coupling of thiol groups, especially of cysteine... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
Kidneys and Regulation of Water and Inorganic Ions
Renal Functions Kidneys remove/add substances from/to the plasma.Regulate water concentration, inorganic ion... Read More
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that... Read More
Myocardium
Myocardium Definition What is the myocardium of the heart? It is the muscular middle layer of the heart that is... Read More
Hemocyanin
Hemocyanin --> haemocyanin (Science: chemical) blue, oxygen transporting, copper containing protein found in the blood of... Read More
Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis Definition Biosynthesis refers to the production (synthesis) of a complex chemical compound from simpler... Read More
Actions of Caffeine in the Brain with Special Reference to Factors That Contribute to Its Widespread Use
IV. Actions of Caffeine on Brain Functions and BehaviorHaving discussed the molecular and neuronal actions of caffeine,... Read More
Flavin adenine dinucleotide
Definition noun plural: flavin adenine dinucleotides fla·vin ad·e·nine di·nu·cle·o·tide, ad·e·nine... Read More