Search Results for: cyclic
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: cyclic adenosine monophosphates (biochemistry) A cyclic form of adenosine monophosphate that... Read More
Cyclic guanosine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: cyclic guanosine monophosphates (biochemistry) A cyclic form of guanosine monophosphate (chemical... Read More
Light-dependent reaction
Many organisms, such as green plants, convert light energy into chemical energy through the mechanism of photosynthesis. In... Read More
Cyclic compound
Cyclic compound Any compound in which the constituent atoms, or any part of them, form a ring. Used mainly in organic... Read More
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physio-chemical process carried out by photo-auto-lithotrophs by converting light energy into chemical... Read More
Prostaglandin
Definition noun, plural: prostaglandins A group of eicosanoids, structurally characterized as 20-carbon unsaturated fatty... Read More
Chlorophyll
Why are most plants green? Have you ever had the same question? Perhaps, you’ve been told that the plants are green... Read More
Guanosine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: guanosine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of guanine, ribose and a phosphate... Read More
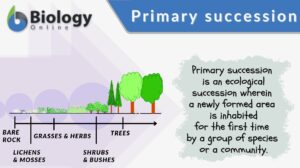
Primary succession
Primary Succession Definition Primary succession is an ecological succession where a newly formed area is inhabited for the... Read More
Nucleotide
Nucleotide Definition A nucleotide is regarded as the basic building block of nucleic acid (e.g. DNA and RNA). A nucleic... Read More
Adenosine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: adenosine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of adenine, ribose and a phosphate... Read More
Chronobiology
Chronobiology Definition Chronobiology is a branch of biology that studies time-related phenomena (e.g., biological... Read More
Adenine nucleotide
Definition noun plural: adenine nucleotides A nucleotide wherein the nucleobase is adenine Details Overview A nucleotide... Read More
Accessory pigment
Definition noun, plural: accessory pigments A non-chlorophyll pigment inside the chloroplast of photosynthetic organisms,... Read More
Light reactions
Definition noun The series of biochemical reactions in photosynthesis that require light energy that is captured by... Read More
Cytidine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: cytidine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of cytosine, ribose and a phosphate... Read More
Plant Metabolism
Introduction Plants are responsible for incredible feats of molecular transformation. The processes are always being... Read More
Polynucleotide
Definition noun plural: polynucleotides pol·y·nu·cle·o·tide, ˌpɒlɪˈno͞o′klē-ə-tīd A biopolymer comprised of... Read More
Thromboxane
Definition noun, plural: thromboxanes Any from the various arachidonic acid metabolites produced by the action of... Read More
Oligonucleotide
Definition noun plural: mononucleotides ol·i·go·nu·cle·o·tide, ŏl′ĭ-gō-no͞o′klē-ə-tīd A short polymer... Read More
Second messenger
second messenger (Science: molecular biology) In many hormone sensitive systems the systemic hormone does not enter the... Read More
Circadian rhythm
Circadian Rhythm Definition A circadian rhythm is an endogenously-driven biological rhythm with a period close to 24... Read More
Photosystem I
Definition noun The photosystem that makes use of light to transfer electron particualrly from plastocyanin to ferredoxin,... Read More
Mononucleotide
Definition noun plural: mononucleotides mon·o·nu·cle·o·tide, ˌmɒnəʊˈnjuːklɪəˌtaɪd A single nucleotide (as... Read More
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine Triphosphate Definition noun plural: adenosine triphosphates (biochemistry) An organic compound that is... Read More
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation Definition We can define phosphorylation as a biochemical process in which a phosphate molecule is added to... Read More
Light-independent reaction
The process of photosynthesis is a biological procedure in which plants produce oxygen and energy (sugar) by using light... Read More
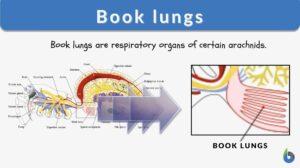
Book lungs
Book Lungs Definition Lungs are known as the organs that help organisms breathe. When we think of lungs, we think of the... Read More
Micromolecule
Micromolecules Definition How to define micromolecule? Micromolecules are relatively small molecules that are combined... Read More
Biological clock
Definition noun, plural: biological clocks Any of the various mechanisms that regulate biological rhythms Supplement A... Read More
Infradian rhythm
What is the Infradian Rhythm? An infradian rhythm is a type of biological rhythm that lasts longer than 24 hours, with a... Read More
Diurnality
Definition noun, plural: diurnalities (1) The condition of occurring or being active during the day (2) The active behavior... Read More
Infective stage
Definition noun (parasitology) The stage in the life cycle of an endoparasite wherein it can initiate infection to its... Read More
Permanent Tattoo Means Permanent Immune Action Of Macrophages
Have you ever wondered why a permanent tattoo seemed to last forever? A simple assumption would be is that the ink could... Read More
Mitochondrial DNA – hallmark of psychological stress
We often hear that stress can be unsettling as it could make us ill when it becomes chronic and overwhelming. However, is... Read More