Search Results for: cytoskeleton
Cytoskeleton
Definition noun plural: cytoskeletons cy·to·skel·e·ton (cell biology) The lattice or internal framework of a cell... Read More
Microtubule
Microtubule Definition noun plural: microtubules mi·cro·tu·bule, mī'krō-tū'byūlA cytoplasmic tubule made up of... Read More
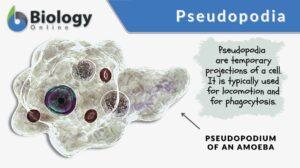
Pseudopodia
A pseudopodium (plural: pseudopodia) refers to the temporary projection of the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell. Pseudopodia... Read More
Intermediate filament
Definition noun plural: intermediate filaments A type of cytoskeleton characterized by having a diameter ranging from 8... Read More
Microfilament
Definition noun plural: microfilaments mi·cro·fil·a·ments, mī'krō-fil'ă-mĕnts A thin, helical, single-stranded... Read More
Intermediate filaments
Definition noun plural: intermediate filaments A type of cytoskeleton characterized by having a diameter ranging from 8... Read More
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis Definition Phagocytosis is a basic physiological cellular process wherein a cell ingests a solid particle... Read More
Plant Cells vs. Animal Cells
Plant Cells Most cells are not visible with the naked eye. However, with microscopes of various types, plant cells can be... Read More
Nuclear matrix
Definition noun plural: nuclear matrices (cell biology) A 3-dimensional filamentous protein network that extends... Read More
Eukaryotic cells
Eukaryotic Cells Definition What is a eukaryotic cell? Eukaryotic cells refer to the cells of (or derived from) eukaryotes,... Read More
Cell Structure
The interior of human cells is divided into the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The nucleus is a spherical or oval-shaped... Read More
Cell membrane
Cell Membrane Definition Just like any non-living body possesses a plastic or paper packaging material that keeps the... Read More
Animal cell
An animal cell is the fundamental functional unit of life of animals. It is also the basic unit of reproduction. Animal... Read More
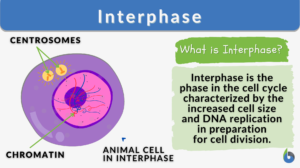
Interphase
Interphase is the critical period in the eukaryotic cell cycle characterized by a sequence of events like the G1 phase where... Read More
Centrosome
Centrosome Definition What is a centrosome? The centrosome is considered to be the main microtubule-organizing... Read More
Sarcolemma
Sarcolemma Definition What is the sarcolemma? It is the thin, transparent, extensible plasma membrane of the muscle cell.... Read More
Axon hillock
Axon Hillock Definition What is axon hillock? If you are familiar with the different parts of the neuron, the axon hillock... Read More
Golgi apparatus
Golgi Apparatus Definition The Golgi apparatus is a membrane-bound organelle in eukaryotic cells. It plays a crucial role... Read More
Nucleoplasm
Definition noun plural: nucleoplasm nu·cle·o·plasm, ˈnjuːklɪəˌplæzəm (cell biology) The protoplasm of the... Read More
Nuclear lamina
Definition noun plural: nuclear laminae or nuclear laminas nu·cle·ar lam·i·na, ˈn(j)ukliɚ ˈlæm.ɪ.nə (cell... Read More
Fibroblast
The building block of living things is known as the cell. The cell contributes to many parts and functions of different... Read More
Selectively-permeable membrane
Selectively Permeable Membrane Definition We can define selectively permeable membranes as those that are selectively... Read More
Cytokinesis
The cell cycle of eukaryotes is a cyclical series of biological events that certain asexual cells go through. The cell cycle... Read More
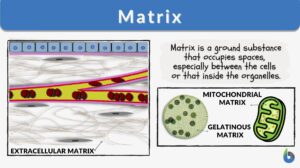
Cell matrix
Definition noun plural: cell matrices cell ma·trix, ˈmeɪtɹɪks An insoluble, dynamic gel in the cytoplasm, believed... Read More
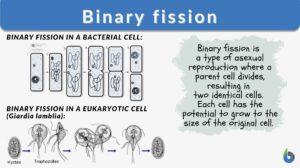
Binary fission
Binary Fission Definition What is binary fission? In biology, binary fission is a type of asexual reproduction where a... Read More
Salmonella typhimurium
Definition A gram-negative pathogenic bacterium associated in gastroenteritis in humans and other... Read More
Tight junction
What are tight junctions? Tight junctions are the intercellular barrier between two neighboring endothelial and epithelial... Read More
Nuclear envelope
Definition noun plural: nuclear envelopes nu·cle·ar en·ve·lope, ˈn(j)ukliɚ ˈɛn.və.ləʊp The two layered membrane... Read More