Search Results for: decay
First-order kinetics
What is a First-Order Kinetics (First-Order Reaction)? First-order kinetics refers to a reaction wherein the overall rate... Read More
Radioactive decay
radioactive decay (Science: physics) The process by which a spontaneous change in nuclear state takes place. This process is... Read More
Nonsense mutation
A nonsense mutation is the type of point mutation that renders the translation process useless by coding for a stop/nonsense... Read More
Decomposer
Decomposer Definition The organisms that carry out the process of decay or breakdown of the dead organism are known as... Read More
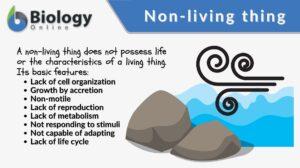
Non-living thing
Non-living Thing Definition A non-living thing in biology means any form without a life, such as an inanimate body or... Read More
Messenger ribonucleic acid
Definition noun plural: messenger ribonucleic acids mes•sen•ger ri•bo•nu•cle•ic ac•id, ˈmɛ.sɪn.dʒəɹ... Read More
Isomaltulose
Definition noun plural: isomaltuloses A disaccharide comprised of a glucose monomer and a fructose monomer joined by... Read More
Decomposition
Definition noun The process or act of breaking down an organic material or substance into smaller constituent parts,... Read More
Putrefaction
putrefaction 1. The act or the process of putrefying; the offensive decay of albuminous or other matter. Putrefaction is a... Read More
Electroporation
Definition noun, plural: electroporations A non-chemical method that transfers the genetic material into the recipient cell... Read More
Net primary productivity
In order to keep the biosphere running, different organisms play different roles and functions. Some help in oxygen... Read More
Balanced diet
What is a balanced diet? What is the definition of a balanced diet? A nutritionally balanced diet fulfills all nutritional... Read More
Nitrogen Cycle
The circulation of nitrogen; nitrates from the soil are absorbed by plants which are eaten by animals that die and decay... Read More
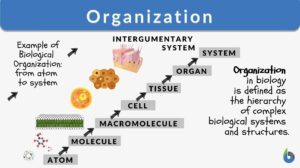
Organization
Organization Definition The meaning of the term "organization" is very simple. It means the state wherein things are... Read More
Fragmentation
Fragmentation Definition What is fragmentation? In general, fragmentation refers to the state or the process of breaking... Read More
Unicellular
Unicellular organisms are organisms consisting of one cell only that performs all vital functions including metabolism,... Read More
Disaccharide
Carbohydrates are organic compounds comprised of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, usually in the ratio of 1:2:1. They are one... Read More
Degenerate
Degenerate means to become worse or less of its kind or former state. In biology, it means an entity performs the same... Read More
Carbon dioxide
Carbon Dioxide Definition noun, car·bon di·ox·ide, /daɪˈɒksaɪd/ (biochemistry) An inorganic compound, with the... Read More
Preservation
preservation The act or process of preserving, or keeping safe; the state of being preserved, or kept from injury,... Read More