Search Results for: decomposition
Decomposer
Decomposer Definition The organisms that carry out the process of decay or breakdown of the dead organism are known as... Read More
Decomposition
Definition noun The process or act of breaking down an organic material or substance into smaller constituent parts,... Read More
Decomposition of movement
Decomposition of movement a manifestation of cerebellar disease in which a muscular movement is not carried out smoothly but... Read More
Redox reaction
Redox Reaction Definition What are redox reactions? This is a common term in chemistry and biology. In chemistry, a redox... Read More
Photodecomposition
Definition noun The decomposition of a chemical compound by means of light energy or photons. Supplement For example, the... Read More
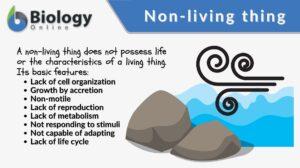
Non-living thing
Non-living Thing Definition A non-living thing in biology means any form without a life, such as an inanimate body or... Read More
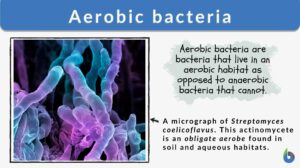
Aerobic bacteria
Aerobic Bacteria Definition What does aerobic mean in biology? As the name suggests, 'aerobe' in biology means organisms... Read More
Recalcitrant
Several words of the English language find wide usage in subjects as diverse as literature, science, social science,... Read More
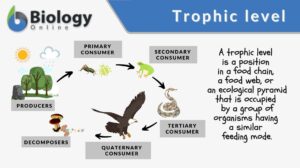
Trophic level
In ecology, a trophic level pertains to a position in a food chain or ecological pyramid occupied by a group of organisms... Read More
Catabolism
Catabolism Definition Catabolism is the branch of the metabolic process that breaks down complex, big molecules into... Read More
First-order kinetics
What is a First-Order Kinetics (First-Order Reaction)? First-order kinetics refers to a reaction wherein the overall rate... Read More
Brief Review on Climate Change and Tropical Peatlands
Peat soils are formed from biochemical process on moderately decomposed vegetation by aerobic microorganisms. It is mostly... Read More
Carbon dioxide
Carbon Dioxide Definition noun, car·bon di·ox·ide, /daɪˈɒksaɪd/ (biochemistry) An inorganic compound, with the... Read More
Biotic factor
Biotic Factor Definition A biotic factor is the living component in an ecosystem. The term "biotic" means "of or related... Read More
Organic matter
Definition noun Any of the carbon-based compounds found in nature Supplement Organic matter pertains to any of the... Read More
Photolysis
Photolysis Definition We define photolysis as a chemical process in which chemical compounds or molecules are split into... Read More
Dehydration reaction
What is dehydration synthesis? A dehydration reaction is a form of biochemical reaction wherein a water molecule is lost or... Read More
Thermophile
Thermophiles Definition What are thermophiles? Let us first understand the literal meaning of the word ‘thermophile’.... Read More
Primary productivity
Planet Earth is home to different types of life forms ranging from microscopic bacteria to giant whales and elephants. To... Read More
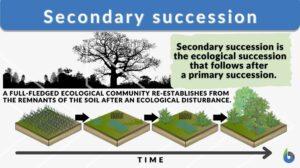
Secondary succession
We all have come across news where forest lands got destroyed by wildfires. Or sometimes we have read about an entire... Read More
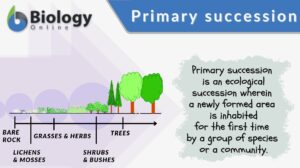
Primary succession
Primary Succession Definition Primary succession is an ecological succession where a newly formed area is inhabited for the... Read More
Methanogen
Definition noun, plural: methanogens An archaeabacterium capable of methanogenesis Supplement A methanogen pertains to any... Read More
Methanogenesis
Definition noun A metabolic process in certain microbes wherein methane is produced Supplement Methanogenesis is a metabolic... Read More
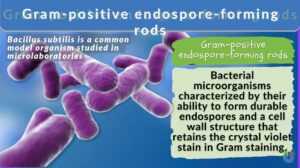
Gram-positive endospore-forming rods
Gram-Positive Endospore-Forming Rods Definition Gram-positive endospore-forming rods are a group of rod-shaped bacteria... Read More
Enzymatic hydrolysis
Definition noun A catalytic decomposition of a chemical compound by reaction with water, such as the conversion of... Read More
Contamination
Contamination Definition Contamination, sometimes interchanged with pollution, is the existence of live things or... Read More
Succession
Definition noun, plural: successions, word origin: Latin "successio" 1. (general) (a) The act of following in order or... Read More
Eubacteria
Eubacteria are prokaryotic microorganisms consisting of a single cell lacking a nucleus and containing DNA is a single... Read More
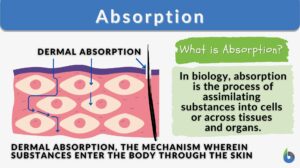
Absorption
Absorption can be defined as the process of assimilating substances across the intestinal epithelial cells or the tissues... Read More