Search Results for: dehydration
Dehydration reaction
What is dehydration synthesis? A dehydration reaction is a form of biochemical reaction wherein a water molecule is lost or... Read More
Voluntary dehydration
voluntary dehydration That physiologic lag or deficit that results when sensations of thirst are not strong enough to bring... Read More
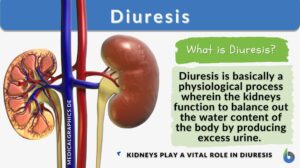
Dehydration
Dehydration The condition that results from excessive loss of body water. Synonym: anhydration, deaquation,... Read More
Carbohydrate
Carbohydrate Definition A biomolecule refers to any molecule that is produced by living organisms. As such, most of them... Read More
Body fluid
Body Fluids Definition What is body fluid? Literally, body fluid is the fluid of the body. The adult human body is ~50-60%... Read More
Hypotonic solution
Hypotonic Solution Definition What is a hypotonic solution? It refers to a solution that contains a lower amount of solute... Read More
Hypertonic
Hypertonic Definition Hypertonic is a term used to describe an entity being in the state of hypertonicity, where there is a... Read More
Saline solution
Saline Solution Definition Saline solution is one the most medically-used solution, which contains sodium chloride... Read More
Hyperosmotic
Hyperosmotic Definition What is hyperosmotic? The word hyperosmotic is derived from two Greek words: 'hyper', meaning... Read More
Heatstroke
Definition noun A severe (sometimes fatal) illness caused by an overexposure to an excessive heat, which disturbs the... Read More
Disaccharide
Carbohydrates are organic compounds comprised of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, usually in the ratio of 1:2:1. They are one... Read More
Polysaccharide
Polysaccharide Definition Biology Definition: A polysaccharide is a carbohydrate formed by long chains of repeating units... Read More
Oligosaccharide
Carbohydrates are organic compounds consisting of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, usually in the ratio of 1:2:1. They are one... Read More
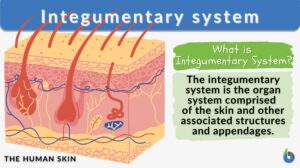
Integumentary system
Integumentary System Definition The integumentary system is the outermost layer of the body. The animal body, in... Read More
Active dry yeast
Definition noun A form of dry yeast in which the yeasts are not killed but made dormant through dehydration, and return to... Read More
Micromolecule
Micromolecules Definition How to define micromolecule? Micromolecules are relatively small molecules that are combined... Read More
Dinucleotide
Definition noun plural: dinucleotides di·nu·cle·o·tide, daɪ njuːklɪəˌtaɪd An organic compound comprised of two... Read More
Cork cambium
Cork Cambium Definition Cork cambium is a secondary meristematic tissue that has a pivotal role in secondary growth in... Read More
Chemosynthesis
Definition noun, plural: chemosyntheses The production of a more complex chemical compound by combining two or more simpler... Read More
Carbon fixation
Carbon Fixation Definition We know that the earth contains many elements. The periodic table shows us just how many... Read More
Glycocalyx
What is the Glycocalyx? The glycocalyx is a polysaccharide-based gel-like, highly hydrous cellular thin layer, covering... Read More
Glycosuria
Definition noun, plural: glycosuria The presence of atypically high sugar level in urine Supplement Glycosuria is a... Read More
Digestion and Absorption of Food
The gastrointestinal (GI) system includes the gastrointestinal tract (mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,... Read More
Vascular plants
Definition of Vascular plants The term 'vascular' is derived from the Latin word vāsculum, vās, meaning "a container and... Read More