Search Results for: endogenous
Endogenous pyrogen
Definition noun, plural: endogenous pyrogens A type of pyrogen produced by activated immune cells, and incite the rise in... Read More
Endogenous
Endogenous (Science: biology) developing or originating within the organisms or arising from causes within the... Read More
Exogenous pyrogen
Definition noun, plural: exogenous pyrogen A type of pyrogen that is of microbial origin, such as the lipopolysaccharide in... Read More
Chronobiology
Chronobiology Definition Chronobiology is a branch of biology that studies time-related phenomena (e.g., biological... Read More
Circadian rhythm
Circadian Rhythm Definition A circadian rhythm is an endogenously-driven biological rhythm with a period close to 24... Read More
Diurnal rhythm
Definition noun, plural: diurnal rhythms A biological rhythm that primarily express a periodicity during daylight... Read More
Infradian rhythm
What is the Infradian Rhythm? An infradian rhythm is a type of biological rhythm that lasts longer than 24 hours, with a... Read More
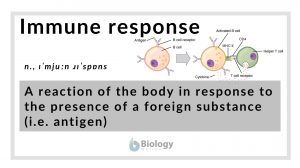
Immune response
Immune Response Definition An immune response is defined as the reaction of the body in response to the presence of a... Read More
Ultradian rhythm
Definition noun, plural: ultradian rhythms A biological rhythm that is repeated throughout a 24-hour circadian day and... Read More
Chronobiologist
Definition noun, plural: chronobiologists A professional or an expert in the field of chronobiology Supplement A... Read More
Methods of Breaking Seed Dormancy
Definition of Seed Dormancy:Non – germination of seeds due to absence of suitable conditions is termed as dormancy.... Read More
Beta-blocker
Definition noun, plural: beta-blockers A drug that blocks the action of endogenous catecholamines on beta-adrenergic... Read More
Biological clock
Definition noun, plural: biological clocks Any of the various mechanisms that regulate biological rhythms Supplement A... Read More
Lipotropin
Definition noun, plural: lipotropins A polypeptide hormone of the anterior pituitary gland, presumably acts by promoting fat... Read More
Cellobiose
Definition noun plural: cellobioses cel·lo·bi·ose, ˌsɛləʊˈbaɪəʊz A disaccharide made up of two glucose... Read More
Liliopsida
Definition noun (plant taxonomy) A taxonomic class of the division Magnoliophyta comprised of lilies, grasses, palms,... Read More
Progestogen
Definition noun, plural: progestogens A steroid hormone that is activated by the binding to the progesterone receptor, and... Read More
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine Triphosphate Definition noun plural: adenosine triphosphates (biochemistry) An organic compound that is... Read More
Regulation of Organic Metabolism, Growth and Energy Balance
Organic Metabolism Events of Absorptive and Post-absorptive States. The absorptive state is the period during which... Read More
FAAH-OUT mutation for a life of no pain – No FAAH, no pain
A Scottish woman claims that she has not experienced pain over some supposedly painful conditions, like a severe joint... Read More
Progesterone
Definition noun, plural: progesterones A progestogen hormone, with a chemical formula of C21H30O2, naturally produced in... Read More
Triple response
Definition noun (immunology) The three cardinal circulatory responses of the skin (i.e. reddening, flare formation or... Read More
Autoantigen
Definition noun, plural: autoantigens An endogenous antigen that is recognized as nonself by the immune system, which should... Read More
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation Definition We can define phosphorylation as a biochemical process in which a phosphate molecule is added to... Read More