Search Results for: enzyme
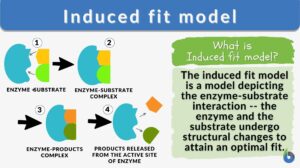
Induced fit model
Induced-Fit Model Definition The induced-fit model is a model for enzyme-substrate interaction to depict the dynamic... Read More
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
Induced enzyme
Induced enzyme Inducible enzyme, an enzyme that can be detected in a growing culture of a microorganism, after the addition... Read More
Ecori restriction enzyme
Ecori restriction enzyme (Science: enzyme molecular biology) a commonly-used restriction enzyme (enzyme which will cleave... Read More
Restriction enzyme
Definition noun, plural: restriction enzymes An enzyme that catalyzes the cleavage of DNA at restriction sites, producing... Read More
Enzyme-substrate complex
Definition noun A non-covalent complex composed of a substrate bound to the active site of the enzyme. Supplement The... Read More
Digestive Enzymes
Have you ever thought about what happens to the food after you have taken it into your mouth? How those big steak pieces... Read More
Reducing enzyme
reducing enzyme --> reductase (Science: enzyme) An enzyme that catalyses a reduction; since all enzymes catalyze... Read More
Enzyme activation
Enzyme activation conversion of an inactive form of an enzyme to one possessing metabolic activity. It includes 1)... Read More
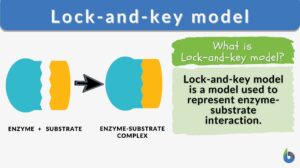
Lock-and-key model
Lock-and-key model Definition Lock-and-key model is a model for enzyme-substrate interaction suggesting that the enzyme and... Read More
Enzyme inhibitors
Enzyme inhibitors compounds or agents that combine with an enzyme in such a manner as to prevent the normal substrate-enzyme... Read More
Marker enzyme
Definition noun, plural: marker enzymes Any enzyme confined to a particular organelle, cell, or cellular... Read More
Lysosomal enzyme
Definition noun plural: lysosomal enzymes ly·so·somal en·zyme, ˈlaɪsəˌsoʊm əl ˈɛnzaɪm (biochemistry) Any of... Read More
Modification enzyme
modification enzyme (Science: enzyme molecular biology) An enzyme that introduces minor bases into dNA or rNA or that alters... Read More
Hydrolytic enzyme
Definition noun, plural: hydrolytic enzymes Any of the enzymes or catalysts that act and behave like a... Read More
Enzyme inactivation
Enzyme inactivation The disappearance of an enzymes activity during in vitro conditions, such as during a lab preparation of... Read More
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that... Read More
Protein Activity and Cellular Metabolism
Protein Binding Sites The ability of various molecules and ions to bind to specific sites on the protein surface forms the... Read More
Constitutive enzyme
Definition noun, plural: constitutive enzymes The enzyme synthesized at a relatively constant level. Supplement These... Read More
Enzyme regulation
Enzyme regulation (Science: biochemistry) control of the rate of a reaction catalyzed by an enzyme by some effector (e.g.,... Read More
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
Nucleotide
Nucleotide Definition A nucleotide is regarded as the basic building block of nucleic acid (e.g. DNA and RNA). A nucleic... Read More
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physio-chemical process carried out by photo-auto-lithotrophs by converting light energy into chemical... Read More
Metalloenzyme
metalloenzyme (Science: enzyme) An enzyme that contains a bound metal ion as part of its structure. The metal may be... Read More
Proteolytic Enzyme
Any enzyme that catalyzes the splitting of proteins into smaller peptide fractions and amino acids by a process known as... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation Definition We can define phosphorylation as a biochemical process in which a phosphate molecule is added to... Read More
Ribonucleotide
Definition noun plural: ribonucleotides ri·bo·nu·cle·o·tide, ˌraɪbəʊˈnjuːklɪəˌtaɪd A form of nucleotide in... Read More