Search Results for: eukaryote
Eukaryotic cells
Eukaryotic Cells Definition What is a eukaryotic cell? Eukaryotic cells refer to the cells of (or derived from) eukaryotes,... Read More
Living things
Living Things Definition A living thing pertains to any organism or a life form that possesses or shows the characteristics... Read More
Prokaryote
Prokaryote refers to any of the group of living organisms primarily characterized by the lack of a true nucleus and other... Read More
Glycosylation
Definition noun A biochemical process where a glycan attaches to a protein, a lipid, or other organic molecule, especially... Read More
Precursor mRNA
Definition noun plural: precursor mRNAs An immature or incompletely processed mRNA molecule in eukaryotes that needs to be... Read More
Brown algae
Brown Algae Definition Brown algae are algal species characterized by being multicellular and having a brown or... Read More
Ribonucleic acid
Ribonucleic Acid Definition noun (uncountable), ribonucleic acids ri·bo·nu·cle·ic ac·id, raɪboʊnjuːkliːɪk... Read More
Ribosomal DNA
Definition noun DNA sequence that codes for ribosomal RNA Supplement Ribosomal DNA is the sequence of DNA that codes for... Read More
Oxidative phosphorylation
Definition noun A metabolic pathway that generates ATP from ADP through phosphorylation that derives the energy from the... Read More
Thermophile
Thermophiles Definition What are thermophiles? Let us first understand the literal meaning of the word ‘thermophile’.... Read More
Chlorophyta
Chlorophyta Definition Chlorophyta is a taxonomic group (a phylum) comprised of green algae that live in marine habitats.... Read More
DNA polymerase
Definition noun, plural: DNA polymerases (molecular biology) An enzyme assisting in DNA replication Supplement Polymerases... Read More
Glycosidase
Definition noun, plural: glycosidases (biochemistry) An enzyme catalyzing the hydrolysis of a... Read More
Gap 0 phase
Definition noun The phase in the cell cycle wherein the cell is in inactive or non-cycling state following cell... Read More
Transposon
Definition noun, plural: transposons A small segment of DNA that is capable of replicating and inserting copies of DNA at... Read More
Phagotrophy
Definition noun A process of ingesting relatively large particles of food that carries out via intracellular... Read More
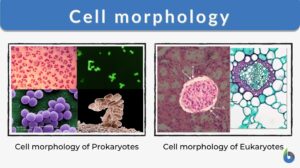
Cell morphology
The basic essence for any living organism is its structural framework which includes appearance, form, and the... Read More
Gap 2 phase
Definition noun (cell biology) A sub-phase in the interphase of the cell cycle wherein the cell continues to grow and then... Read More
Gap 1 phase
Definition noun (cell biology) The first period in the interphase wherein the cell primarily grows in cell... Read More
Eukaryotic cell
Definition noun, plural: eukaryotic cells The cell of a eukaryote, i.e. an organism that possesses a membrane-bound... Read More
Synthesis phase
Definition noun (cell biology) A sub-phase in the interphase wherein the cell primarily duplicates its DNA via... Read More
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid
Definition noun plural: ribosomal ribonucleic acids ri•bo•so•mal ri•bo•nu•cle•ic ac•id, ˈraɪ... Read More
Gap 2-M DNA damage checkpoint
Definition noun (cell biology) A control mechanism in G2 phase of the cell cycle that ensures the cell is ready for cell... Read More
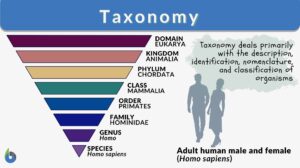
Primitive Animals
Incorrect taxonomic classifications deemed organisms to be either animals or plants, in the Plantae or Animalia kingdoms... Read More
Perfect fungi
Definition noun A group of fungi that reproduce through asexual spores and sexually-produced spores Supplement Fungi are... Read More
Retrotransposon
Definition noun, plural: retrotransposons A transposon that is amplified via reverse transcription, i.e. the DNA element is... Read More
Interspersed repeat
Definition noun, plural: interspersed repeats A type of repeated sequence in which the copies are dispersed throughout the... Read More
Proteinoplast
Definition noun, plural: proteinoplasts (botany) A leucoplast that stores and modifies protein Supplement Plastids are... Read More
Gerontoplast
Definition noun, plural: gerontoplasts A plastid that forms from chloroplast during senescence Supplement Plastids are... Read More
Chromomere
Definition noun, plural: chromomeres (genetics) One of the beadlike granules that are arranged in a linear series along the... Read More
Endomembrane system
Ever wondered how biomolecules are made within the cell and then they are released outside the cell for use by the body?... Read More
Extracellular inheritance
Definition noun A form of non-Mendelian inheritance in which a trait was transmitted from the parent to offspring through... Read More