Search Results for: exogenous
Exogenous pyrogen
Definition noun, plural: exogenous pyrogen A type of pyrogen that is of microbial origin, such as the lipopolysaccharide in... Read More
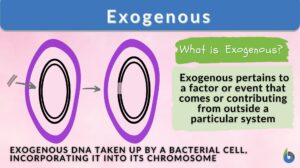
Exogenous antigen
Definition noun Antigen that enters the body of the organism from the outside, e.g. through inhalation, ingestion, or... Read More
Chronobiology
Chronobiology Definition Chronobiology is a branch of biology that studies time-related phenomena (e.g., biological... Read More
Ultradian rhythm
Definition noun, plural: ultradian rhythms A biological rhythm that is repeated throughout a 24-hour circadian day and... Read More
Infradian rhythm
What is the Infradian Rhythm? An infradian rhythm is a type of biological rhythm that lasts longer than 24 hours, with a... Read More
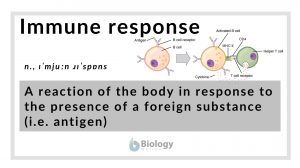
Immune response
Immune Response Definition An immune response is defined as the reaction of the body in response to the presence of a... Read More
Diurnal rhythm
Definition noun, plural: diurnal rhythms A biological rhythm that primarily express a periodicity during daylight... Read More
Endogenous pyrogen
Definition noun, plural: endogenous pyrogens A type of pyrogen produced by activated immune cells, and incite the rise in... Read More
Biological clock
Definition noun, plural: biological clocks Any of the various mechanisms that regulate biological rhythms Supplement A... Read More
Glycogenesis
Definition noun The metabolic process of producing glycogen from glucose for storage mainly in liver and muscle cells in... Read More
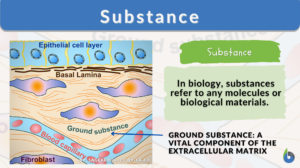
Carbohydrate
Carbohydrate Definition A biomolecule refers to any molecule that is produced by living organisms. As such, most of them... Read More
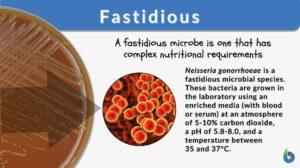
Fastidious
Fastidious Definition We can define fastidious as a term used in microbiology to denote a species that lacks the ability to... Read More
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine Triphosphate Definition noun plural: adenosine triphosphates (biochemistry) An organic compound that is... Read More
Self antigen
Definition noun, plural: self antigens An exogenous antigen that is recognized as nonself by the immune system, which should... Read More
Polysaccharide
Polysaccharide Definition Biology Definition: A polysaccharide is a carbohydrate formed by long chains of repeating units... Read More
Methods of Breaking Seed Dormancy
Definition of Seed Dormancy:Non – germination of seeds due to absence of suitable conditions is termed as dormancy.... Read More
Transgenesis
Definition noun The process of introducing transgene from one organism into another (unrelated) organism or... Read More
Electrotropism
Definition noun Growth or movement of a cell or an organism in response to an electric field Supplement In general, tropism... Read More
Transgenic
Definition adjective Of, pertaining to, or relating to an organism that has genes from another organism put into its genome... Read More
Recombination DNA repair
Recombination DNA Repair Definition Recombination DNA repair is a biological reparative process in response to DNA damage... Read More
Circadian rhythm
Circadian Rhythm Definition A circadian rhythm is an endogenously-driven biological rhythm with a period close to 24... Read More
Hepatocyte
Definition noun, plural: hepatocytes Any of the large, polygonal-shaped cells in the liver. Supplement Hepatocytes are the... Read More
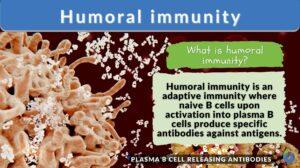
Humoral immunity
Let’s get to know where one should place humoral immunity, the topic of today’s discussion!! By the end of the article,... Read More
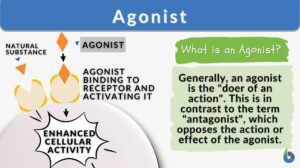
Growth inhibitors
Growth inhibitors endogenous or exogenous substances which inhibit the normal growth of human and animal cells or... Read More