Search Results for: fatal
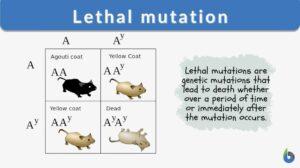
Lethal mutation
Lethal Mutation Definition Genetic mutations come from changes in the DNA structure or sequencing in an organism. Often... Read More
Smooth muscle
The smooth muscle can be described as a type of muscle in the human body that is non-striated and involuntary in action.... Read More
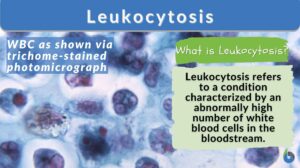
Leukocytosis
What Is Leukocytosis? Leukocytosis is a condition wherein the number of White Blood Cells (WBCs) is increased above the... Read More
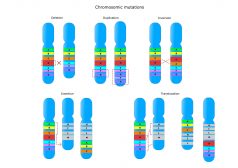
Chromosome Mutations
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D.By nature, the genetic information from both parents is expected to be seen... Read More
Hypertonic solution
Hypertonic Solution Definition Hypertonic solution is a relative term that describes the solution having a higher amount of... Read More
Water in Plants
The movement of molecules, specifically water and any solutes, is vital to understand in light of plant processes. This will... Read More
Plant Tissues
Plants are composed of three major organ groups: roots, stems, and leaves. As we know from other areas of biology, these... Read More
Naegleria fowleri
Naegleria fowleri (commonly referred to as the brain-eating amoeba) is a heat-loving amoeboflagellate protozoan of the... Read More
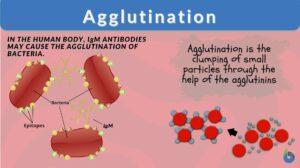
Agglutination
Agglutination Definition What does agglutination mean? It generally refers to the process of sticking together or the... Read More
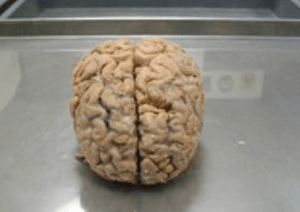
Types and Causes of Brain Damage
The brain is a highly specialized tissue, far more complex than today's 21st-century supercomputers. Due to this magnificent... Read More
Saline solution
Saline Solution Definition Saline solution is one the most medically-used solution, which contains sodium chloride... Read More
Vibrio cholerae
Definition Noun A gram-negative single polar flagellum bacterium associated with cholera infection in... Read More
Scientists brought dead pig brain partly back to life
Death is inevitable to any entity that has life. When there is a beginning there ought to be an end. However, the recent... Read More
Phospholipid
What is a phospholipid? Phospholipids are a subgroup of lipids. Other major types of lipids are fatty acids, sphingolipids,... Read More
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (sER) is part of or a region in the endoplasmic... Read More
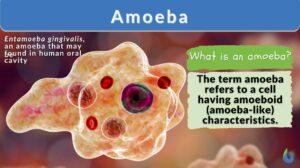
Amoebic dysentery
Definition noun A form of dysentery in which the causative agent is an amoeba, particularly Entamoeba... Read More
Reservoir host
Reservoir Host Definition A reservoir host is a host that harbors the pathogen and serves as a source of the infective... Read More
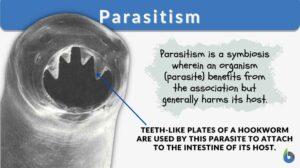
Parasitism
Organisms depend on different sources of food to survive. Larger organisms like plants make their own food (autotrophs) and... Read More
Dinoflagellate
A dinoflagellate is a flagellate algae characterized by their two flagella of unequal length. One of the flagella is lying... Read More
Tertian fever
tertian fever --> vivax malaria (Science: disease, microbiology) A type of malaria caused by the protozoan plasmodium... Read More
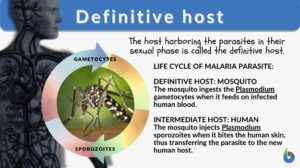
Definitive host
Different Biological Relationships The biological world is interconnected whether we notice it or not. All the life forms... Read More
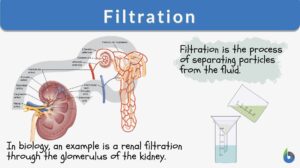
Filtration
Filtration Definition What is filtration? Filtration is separating a solid from a fluid through a porous material that... Read More
Frameshift mutation
Define Frameshift Mutation What is a frameshift mutation? In biology, insertions or deletions of nucleotides in the coding... Read More
Cell adhesion
Cell Adhesion Definition Cell adhesion is the process in which a cell uses a specialized complex of proteins to get... Read More
Heatstroke
Definition noun A severe (sometimes fatal) illness caused by an overexposure to an excessive heat, which disturbs the... Read More
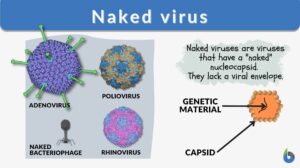
Naked virus
Viruses are infectious entities with size ranges between 20 to 400 nanometers. The mammoth-sized virus would be about the... Read More