Search Results for: gel
Electrophoresis
Electrophoresis (Science: technique) separation of ionic molecules, (principally proteins) by the differential migration... Read More
Glycocalyx
What is the Glycocalyx? The glycocalyx is a polysaccharide-based gel-like, highly hydrous cellular thin layer, covering... Read More
Cell matrix
Definition noun plural: cell matrices cell ma·trix, ˈmeɪtɹɪks An insoluble, dynamic gel in the cytoplasm, believed... Read More
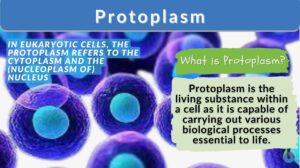
Protoplasm
Protoplasm Definition The protoplasm is regarded as "the living material or the living content of a cell". It is fluid... Read More
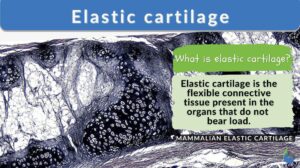
Elastic cartilage
The cartilage is a connective tissue characterized by having an extracellular matrix that is abundant in chondroitin sulfate... Read More
Maxam-Gilbert sequencing
Definition noun A DNA sequencing technique developed in 1976-1977 by Allan Maxam and Walter Gilbart to identify the sequence... Read More
Proteoglycan
What are proteoglycans? Proteoglycans are primarily a type of polysaccharide. Structurally, proteoglycans are... Read More
Vitreous humor
Definition noun The clear, gel-like body fluid in the vitreous chamber, i.e. the posterior cavity between the lens and the... Read More
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that... Read More
Karyolymph
Karyolymph The presumably fluid substance or gel of the nucleus in which stainable elements were believed to be suspended;... Read More
Dna sequence analysis
Dna sequence analysis (Science: molecular biology) determination of the nucleotide Sequence of a length of dna. Typically,... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More
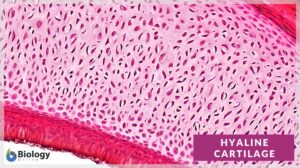
Hyaline cartilage
Hyaline Cartilage Definition Before we define hyaline cartilage, let us understand what cartilage is. What is cartilage? Is... Read More
Reducing sugar
Reducing Sugar Definition What is reducing sugar? The type of sugar that acts as the reducing agent and can effectively... Read More
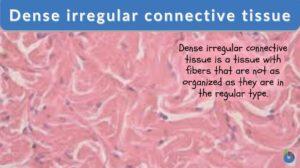
Dense irregular connective tissue
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue Definition Dense irregular connective tissue is one of the two major types of dense... Read More
Cytoplasmic matrix
Definition noun singular: cytoplasmic matrices cy·to·plas·mic ma·trix (1) Synonym for cell matrix, an insoluble,... Read More
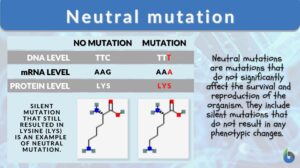
Neutral mutation
Neutral Mutation Definition What is a neutral mutation? Neutral mutations are the alterations in the DNA that are... Read More
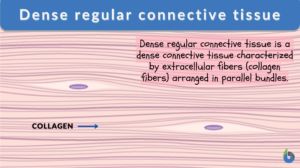
Dense regular connective tissue
The dense connective tissue is a type of connective tissue proper that consists predominantly of fibers, especially type I... Read More
Reticular connective tissue
Definition noun A type of connective tissue characterized by the predominance of reticular fibers made of type III collagen... Read More
Radial immunodiffusion
Definition noun A quantitative immunodiffusion technique used to detect the level of protein (antigen) in a sample by... Read More
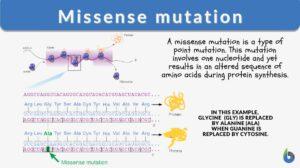
Missense mutation
What is a missense mutation? Literally speaking, a mutation that changes the meaning of the encoded gene sequence is the... Read More
Locomotion
Definition noun The ability of cells or organisms to move and propel itself from place to place Supplement Locomotion in... Read More
Coagulation
Definition noun, plural: coagulations (haematology) The process of clot formation (surgery) The disruption of tissue by... Read More
Transformation
Definition noun, plural: transformations (1) The act, state or process of changing, such as in form or structure; the... Read More
Desiccation
Desiccation definition Desiccation refers to the state, the act, or the process of removing or extracting water content... Read More
Cell adhesion
Cell Adhesion Definition Cell adhesion is the process in which a cell uses a specialized complex of proteins to get... Read More
Fibroblast
The building block of living things is known as the cell. The cell contributes to many parts and functions of different... Read More