Search Results for: glycogen
Glycogenosis
Definition noun, plural: glycogenoses A metabolic disorder caused by a defective glycogen metabolism resulting in the extra... Read More
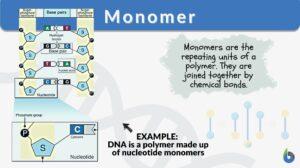
Glycogenesis
Definition noun The metabolic process of producing glycogen from glucose for storage mainly in liver and muscle cells in... Read More
Glycogenolysis
Definition noun The metabolic process of breaking down stored glycogen in liver into glucose subunits (i.e.... Read More
Polysaccharide
Polysaccharide Definition Biology Definition: A polysaccharide is a carbohydrate formed by long chains of repeating units... Read More
Carbohydrate
Carbohydrate Definition A biomolecule refers to any molecule that is produced by living organisms. As such, most of them... Read More
Sugar Homeostasis
Blood Sugar Regulation As described in Cell Biology tutorials, the body requires volumes of glucose in order to create ATP.... Read More
Regulation of Organic Metabolism, Growth and Energy Balance
Organic Metabolism Events of Absorptive and Post-absorptive States. The absorptive state is the period during which... Read More
Monosaccharide
Monosaccharide Definition In biology and biochemistry, a monosaccharide is a simple sugar that constitutes the building... Read More
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
Catabolism
Catabolism Definition Catabolism is the branch of the metabolic process that breaks down complex, big molecules into... Read More
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (sER) is part of or a region in the endoplasmic... Read More
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation Definition We can define phosphorylation as a biochemical process in which a phosphate molecule is added to... Read More
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the tendency not to stray from the range of favorable or ideal internal conditions. Such conditions must be... Read More
Protein Activity and Cellular Metabolism
Protein Binding Sites The ability of various molecules and ions to bind to specific sites on the protein surface forms the... Read More
A Balanced Diet – Carbohydrates and Fat
Alongside the numerous vitamins that are required as part of a healthy diet, we must also eat food containing a variety of... Read More
Amylopectin
Definition noun, plural: amylopectin A polysaccharide made up of highly-branched polymer of alpha-glucose units, and is a... Read More
Skeletal muscle
Definition noun, plural: skeletal muscles A voluntary, striated (vertebrate) muscle that is associated with the skeleton,... Read More
Metabolism
Metabolism Definition What is metabolism in the body? Metabolism encompasses the various biochemical processes, reactions,... Read More
Saccharide
Saccharide Definition What is a saccharide molecule? A saccharide is the unit structure of carbohydrates. In biochemistry,... Read More
Uridine triphosphate
Definition noun plural: uridine triphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of uracil, ribose and three phosphate... Read More
Dehydration reaction
What is dehydration synthesis? A dehydration reaction is a form of biochemical reaction wherein a water molecule is lost or... Read More
Muscular system
Muscular System Definition What is the muscular system? The muscular system is a system that includes muscle cells and... Read More
Lysosomal enzyme
Definition noun plural: lysosomal enzymes ly·so·somal en·zyme, ˈlaɪsəˌsoʊm əl ˈɛnzaɪm (biochemistry) Any of... Read More
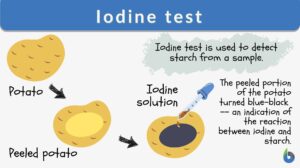
Iodine test
Iodine Test Definition The iodine test is a chemical reaction-based identification test for starch. In this test, iodine... Read More
Gluconeogenesis
Definition noun The metabolic process in which glucose is formed from non-carbohydrate precursors Supplement Glucose is an... Read More
An introduction to Homeostasis
Researched and Written by Jonjo MinnsSubmitted to biologyonline.com on February 25, 2009.Published in biologyonline.com... Read More
Disaccharide
Carbohydrates are organic compounds comprised of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, usually in the ratio of 1:2:1. They are one... Read More
Limit dextrin
Limit dextrin The polysaccharide fragments remaining at the end (limit) of exhaustive hydrolysis of amylopectin or glycogen... Read More