Search Results for: half-life
First-order kinetics
What is a First-Order Kinetics (First-Order Reaction)? First-order kinetics refers to a reaction wherein the overall rate... Read More
Redox reaction
Redox Reaction Definition What are redox reactions? This is a common term in chemistry and biology. In chemistry, a redox... Read More
Phosphodiester bond
Phosphodiester Bond Definition Phosphodiester bonds are the backbone of the strands of nucleic acid present in the life... Read More
The FIFTH MIRACLE: The Search for the Origin and Meaning of Life
The FIFTH MIRACLE: The Search for the Origin and Meaning of Life ... Read More
Meiosis and Alternation of Generations
Review of Mitosis: Cell Cycle The cell cycle contains the process in which cells are either dividing or in between... Read More
Reproduction
Reproduction Definition Reproduction is a biological phenomenon of producing offspring/s. i.e. more of its kind. Depending... Read More
Parthenogenesis
To reproduce, by definition, means to produce new offspring. The process is referred to as reproduction, which is one of the... Read More
Secular equilibrium
secular equilibrium A type of radioactive equilibrium in which the half-life of the precursor (parent) radioisotope is so... Read More
Types and Causes of Brain Damage
The brain is a highly specialized tissue, far more complex than today's 21st-century supercomputers. Due to this magnificent... Read More
Demographic transition
The demographic transition model is a theoretical framework that explains the historical shift in population dynamics as a... Read More
Sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a mode of reproduction involving the fusion of haploid female gamete (egg cell) and haploid male... Read More
Primitive Animals
Incorrect taxonomic classifications deemed organisms to be either animals or plants, in the Plantae or Animalia kingdoms... Read More
Balanced diet
What is a balanced diet? What is the definition of a balanced diet? A nutritionally balanced diet fulfills all nutritional... Read More
Nervous System
THE is the most complicated and highly organized of the various systems which make up the human body. It is the... Read More
Cell division
Cell division is a biological process by which a parent cell duplicates its cell contents and divides to give rise to two or... Read More
Biodiversity
Biodiversity Lead Author: J. Emmett DuffyThis article has been reviewed and approved by the following Topic Editor: John... Read More
Cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria Definition Cyanobacteria is a group of photosynthetic bacteria widely distributed in various aquatic habitats... Read More
Pharmacology
Definition noun The branch in medicine that deals with the study of drugs, especially their action, use, preparation, and... Read More
Radioactive atom
Radioactive atom (Science: chemistry, physics) An atom with an unstable nucleus, which emits particulate or electromagnetic... Read More
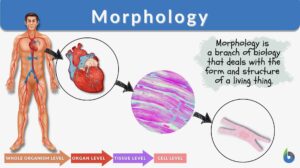
Morphology
Morphology Definition Morphology means the study of the shape and structure of living things from a biological perspective.... Read More
Primary productivity
Planet Earth is home to different types of life forms ranging from microscopic bacteria to giant whales and elephants. To... Read More