Search Results for: hiv
HSV-2- and HIV-1- permissive cell lines co-infected by HSV-2 and HIV-1 co-replicate HSV-2 and HIV-1 without production of HSV-2/HIV-1 pseudotype particles
Jérôme LeGoff1, Hicham Bouhlal1, Maxime Lecerf1, Christophe Klein2, Hakim Hocini1, Ali Si-Mohamed1, Martin Muggeridge3 and... Read More
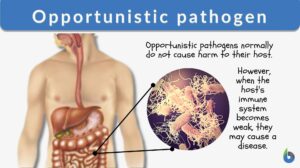
Opportunistic pathogen
Opportunistic Pathogen Definition How do we define opportunistic pathogen? The opportunistic pathogen is an infectious... Read More
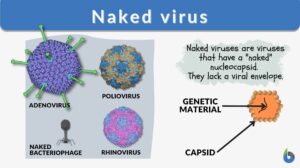
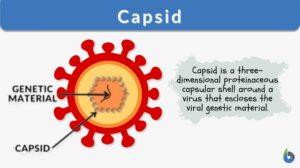
Naked virus
Viruses are infectious entities with size ranges between 20 to 400 nanometers. The mammoth-sized virus would be about the... Read More
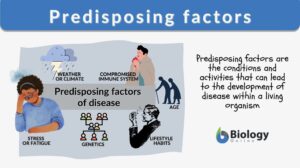
Predisposing factors
All organisms can be born with or develop a disease at any point in their lifetime. When someone is born with a disease, it... Read More
Silent mutation
A mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene or a chromosome. When there is only one nucleotide involved, it... Read More
Pathogenicity
Definition noun, plural: pathogenicities The capability (of a pathogenic agent) to cause disease Supplement Pathogenicity... Read More
Deoxythymidine
Definition noun plural: deoxythymidines A pyrimidine nucleoside that has thymine attached to the pentose sugar... Read More
Genetic variability
Genetic Variability Definition Genetic variability refers to the tendency of individual genetic characteristics in a... Read More
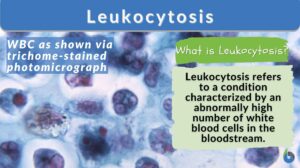
Leukocytosis
What Is Leukocytosis? Leukocytosis is a condition wherein the number of White Blood Cells (WBCs) is increased above the... Read More
Protein pump
Protein pump - a kind of protein that is capable of pumping out compounds that could pose a threat to the cell. An example... Read More
Complementary DNA
Definition noun A double stranded DNA produced from the messenger RNA synthesis in a reaction catalyzed by an enzymes... Read More
Body fluid
Body Fluids Definition What is body fluid? Literally, body fluid is the fluid of the body. The adult human body is ~50-60%... Read More
Demographic transition
The demographic transition model is a theoretical framework that explains the historical shift in population dynamics as a... Read More
Translation
Translation, in general, is the conversion of something into another form, such as a word from one language to another. But... Read More
RNA-dependent DNA polymerase
Definition noun A DNA polymerase enzyme that catalyzes the process of reverse transcription. Supplement This enzyme... Read More
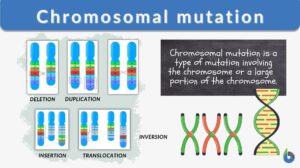
Chromosomal mutation
Every living thing is made up of DNA. Our DNA is what makes us unique and different in the world. Our DNA is made up of... Read More
Color Atlas & Synopsis of Clinical Dermatology
Color Atlas & Synopsis of Clinical Dermatology ... Read More
Visna maedi virus
Visna maedi virus (Science: virology) A retrovirus of sheep and goats. A member of the lentivirus subfamily related to... Read More
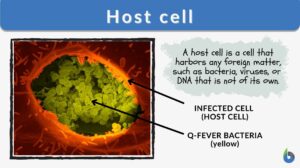
Immunodeficiency
Immunodeficiency Inabillity to mount a normal immune response. Immunodeficiency can be due to a genetic disease or acquired... Read More
Vertical transmission
vertical transmission (Science: microbiology) transmission of a pathogen such as hIV from mother to foetus or baby during... Read More
Frameshift mutation
Define Frameshift Mutation What is a frameshift mutation? In biology, insertions or deletions of nucleotides in the coding... Read More
Incubation period
Incubation Period Definition The incubation period is the time duration between exposure to the pathogen and the appearance... Read More
Retrovirus
Definition noun, plural: retroviruses Any of the group of viruses in the family Retroviridae. The virus is characterized by... Read More
Transactivation
Definition noun, plural: transactivations (molecular biology, genetics) The stimulation of transcription by expressing an... Read More
Adipose tissue
Adipose Tissue Definition Adipose tissue, a specialized variety of connective tissue, is composed of lipid-rich cells known... Read More