Search Results for: immunology
Immunology
Immunology (Science: study) a subfield of biology that deals with the study of antigens and the immuneprocess and how humans... Read More
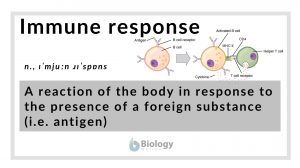
Immune response
Immune Response Definition An immune response is defined as the reaction of the body in response to the presence of a... Read More
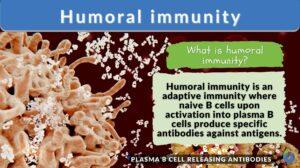
Humoral immunity
Let’s get to know where one should place humoral immunity, the topic of today’s discussion!! By the end of the article,... Read More
Triple response
Definition noun (immunology) The three cardinal circulatory responses of the skin (i.e. reddening, flare formation or... Read More
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis Definition Phagocytosis is a basic physiological cellular process wherein a cell ingests a solid particle... Read More
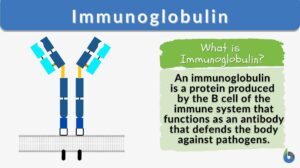
Immunoglobulin
Immunoglobulin Definition An immunoglobulin is a globulin molecule produced by the immune cells, for the body's defense... Read More
Neutralization
Definition noun (general) The act or process of making neutral. (chemistry) A chemical reaction in which an acid and a base... Read More
Complement fixation test
Definition noun (immunology) A form of immunological test for the detection of the presence of either a particular antibody... Read More
Active agglutination
Definition noun An agglutination reaction in which the antigen is found naturally on particle Supplement Agglutination... Read More
Antigenic variation
Definition noun, plural: antigenic variations (immunology) The changing of surface proteins by an infectious agent to evade... Read More
Alloimmunity
Definition noun, plural: alloimmunities (immunology) A type of immunity that produces an immune response that is attacking... Read More
Microbiology
Definition noun The branch of science that deals with microorganisms and their effects on other living... Read More
Mitochondrion
Mitochondrion Definition What are mitochondria? The term “mitochondrion” comes from the two words of the Greek... Read More
Anaphylactic shock
Anaphylactic shock (Science: immunology) a serious, often life-threatening allergic reaction that is characterised by low... Read More
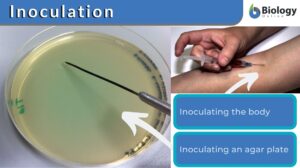
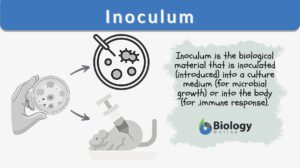
Inoculation
Inoculation Definition In Immunology, inoculation is defined as the process of introducing an antigenic substance or... Read More
Reverse passive agglutination
Definition noun A type of agglutination reaction in which known antibody is bound to a carrier particle instead of the... Read More
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that... Read More
Autoimmunity
Definition noun, plural: autoimmunities A type of immunity wherein the immune response is directed against own body,... Read More
Monoclonal antibody
monoclonal antibody (Science: immunology molecular biology) A substance, usually a protein, which can be synthsised in the... Read More
Polyvalent
Definition adjective (immunology) Of or pertaining to having several antibodies each capable of destroying or inactivating a... Read More
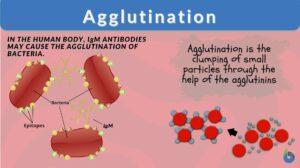
Agglutination
Agglutination Definition What does agglutination mean? It generally refers to the process of sticking together or the... Read More
HSV-2- and HIV-1- permissive cell lines co-infected by HSV-2 and HIV-1 co-replicate HSV-2 and HIV-1 without production of HSV-2/HIV-1 pseudotype particles
Jérôme LeGoff1, Hicham Bouhlal1, Maxime Lecerf1, Christophe Klein2, Hakim Hocini1, Ali Si-Mohamed1, Martin Muggeridge3 and... Read More
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER or rER) is a membrane-bound organelle... Read More
Complement
Complement (Science: immunology) a term originally used to refer to the heat labile factor in serum that causes immune... Read More