Search Results for: ligand
Ligand gated ion channels
Ligand gated ion channel a transmembrane ion channel whose permeability is increased by the binding of a specific ligand,... Read More
Protein Activity and Cellular Metabolism
Protein Binding Sites The ability of various molecules and ions to bind to specific sites on the protein surface forms the... Read More
Monod-Wyman-Changeux model
Definition noun (biochemistry) A model used to describe the allosteric forms of cooperativity Supplement The... Read More
Affinity chromatography
Affinity chromatography (Science: investigation) a technique of analytical chemistry used to separate and purify a... Read More
Down-regulation
Down-regulation (Science: physiology) development of a refractory or tolerant state consequent upon repeated administration... Read More
Saturation of receptors
saturation of receptors saturation, the state in which all receptors are effectively occupied all the time, can be said to... Read More
Gated ion channel
(Science: physiology) transmembrane proteins of excitable cells, that allow a flux of ions to pass only under defined... Read More
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation Definition We can define phosphorylation as a biochemical process in which a phosphate molecule is added to... Read More
Chelating agent
Definition noun, plural: chelating agents A ligand, often an organic compound, which reacts with a metal ion to produce a... Read More
Movement of Molecules Across Cell Membranes
Diffusion Diffusion is essentially the movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower... Read More
Beta barrel
Definition noun, plural: beta barrels A large β-sheet that twists and coils to form a closed structure where the first... Read More
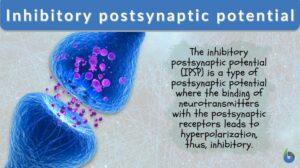
Inhibitory postsynaptic potential
Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential Definition An inhibitory postsynaptic potential is a type of synaptic potential. It is... Read More
Extrinsic pathway
Definition noun (1) (hematology) One of the two initial pathways for the conversion of the prothrombin to thrombin in the... Read More
Proteoglycan
What are proteoglycans? Proteoglycans are primarily a type of polysaccharide. Structurally, proteoglycans are... Read More
Gynaecophore
Definition noun, plural: gynecophores A receptacle, often in the ventral body, of certain adult male animals (dioecious... Read More
Glycosaminoglycan
Definition noun (biochemistry) The polysaccharide unit of proteoglycan Supplement Glycosaminoglycans are the polysaccharide... Read More
Up-regulation physiology
up-regulation (physiology) process that increases ligand/receptor interactions due to an increase in the number of available... Read More
Active centre
Active centre The part of a macromolecule at which a substrate or ligand, upon binding, produces biological activity; for an... Read More
Dissociation constant
Definition noun (1) A mathematical constant that describes the tendency of a large molecule to dissociate reversibly into... Read More
Adair-koshland-nemethy-filmer model
Adair-koshland-nemethy-filmer model --> Koshland-Nemethy-Filmer model (Science: biochemistry, chemistry) a model to... Read More
Competitive binding assay
Definition An assay based on the competition between labeled and unlabeled ligand for the reactive sites of a particular... Read More
Hill coefficient
Hill coefficient a measure of cooperativity in a binding process. a hill coefficient of 1 indicates independent binding, a... Read More
Modulation
modulation --> neuromodulation alteration in the effectiveness of voltage gated or ligand gated ion channels by changing... Read More
Conformational change
Conformational change (Science: cell biology) alteration in the shape usually the tertiary structure of a protein as a... Read More