Search Results for: lipid
Phospholipid
What is a phospholipid? Phospholipids are a subgroup of lipids. Other major types of lipids are fatty acids, sphingolipids,... Read More
Sphingolipid
Definition noun plural: sphingolipids sphin·go·lip·id A type of lipid with a sphingoid base (e.g. sphingosine and... Read More
Fluid mosaic model
Fluid Mosaic Model Definition What is the fluid mosaic model? The fluid mosaic model is a three-dimensional representation... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
Phospholipid bilayer
Definition noun The two layers of phospholipids arranged in such a way that their hydrophobic tails are projecting inwards... Read More
Glyceroglycolipid
Definition noun, plural: glyceroglycolipids A type of glycolipid made up of an acetylated or non-acetylated glycerol and at... Read More
Annular lipid
Annular lipid The layer(s) of lipid bound to and/or surrounding an integral membrane... Read More
Cell membrane
Cell Membrane Definition Just like any non-living body possesses a plastic or paper packaging material that keeps the... Read More
Amphipathic
Amphipathic Definition Amphipathic is a word used to describe a chemical compound containing both polar (water-soluble) and... Read More
Metabolism
Metabolism Definition What is metabolism in the body? Metabolism encompasses the various biochemical processes, reactions,... Read More
Plasma membrane
Do all cells have a plasma (or cell) membrane? Yes, all cells have a biological membrane that separates the protoplasm from... Read More
Glycerolipid
Definition noun, plural: glycerolipids A type of lipid made up of a glycerol linked esterically to a fatty acid Supplement A... Read More
Glycosphingolipid
Definition noun, plural: glycosphingolipids A type of glycolipid made up of a glycan (or a carbohydrate) linked to the... Read More
Glycolipid
Definition noun, plural: glycolipids A carbohydrate, usually an oligosaccharide, that is covalently linked to a lipid... Read More
Endomembrane system
Ever wondered how biomolecules are made within the cell and then they are released outside the cell for use by the body?... Read More
Prokaryote
Prokaryote refers to any of the group of living organisms primarily characterized by the lack of a true nucleus and other... Read More
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (sER) is part of or a region in the endoplasmic... Read More
Golgi apparatus
Golgi Apparatus Definition The Golgi apparatus is a membrane-bound organelle in eukaryotic cells. It plays a crucial role... Read More
Lipogenesis
Lipogenesis Definition Lipogenesis is the process of producing lipid or fat to store biochemical energy for later metabolic... Read More
Sphingolipidosis
Definition noun, plural: sphingolipidoses A lysosomal disease due to an abnormal sphingolipid... Read More
Biomolecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral, group of atoms that can exist alone in a free state while its characteristic... Read More
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER or rER) is a membrane-bound organelle... Read More
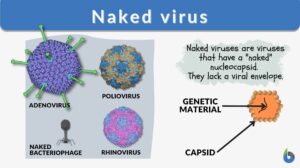
Naked virus
Viruses are infectious entities with size ranges between 20 to 400 nanometers. The mammoth-sized virus would be about the... Read More
Fatty acid
Definition noun plural: fatty acids'' fatty acid, ˈfætɪ ˈæsɪd Any of the group of a long chain of hydrocarbon... Read More
Adipose tissue
Adipose Tissue Definition Adipose tissue, a specialized variety of connective tissue, is composed of lipid-rich cells known... Read More
Facilitated diffusion
Facilitated diffusion is the transport of substances across a biological membrane from an area of higher concentration to an... Read More
Oligosaccharide
Carbohydrates are organic compounds consisting of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, usually in the ratio of 1:2:1. They are one... Read More
Selectively-permeable membrane
Selectively Permeable Membrane Definition We can define selectively permeable membranes as those that are selectively... Read More
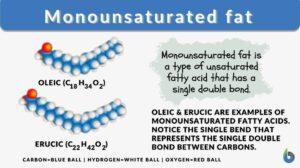
Monounsaturated fat
What is monounsaturated fat? Monounsaturated fats are healthy dietary fats. They are liquid at room temperature. Unlike... Read More
Glycosylation
Definition noun A biochemical process where a glycan attaches to a protein, a lipid, or other organic molecule, especially... Read More
Pinocytosis
Pinocytosis Definition What is pinocytosis? Pinocytosis is the ingestion of extracellular fluids, i.e. the fluid... Read More