Search Results for: liver
Bare area of liver
Bare area of liver The area on the posterior surface of the liver which is fused with the diaphragm and therefore not... Read More
Kupffer cell
Definition noun, plural: Kupffer cells A specialized stellate macrophage cell that is located fixedly within the liver... Read More
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
Regulation of Organic Metabolism, Growth and Energy Balance
Organic Metabolism Events of Absorptive and Post-absorptive States. The absorptive state is the period during which... Read More
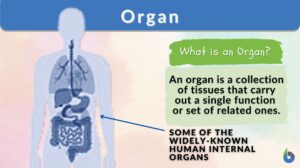
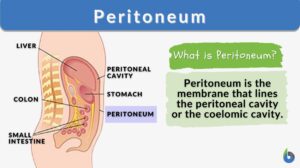
Peritoneum
What is the Peritoneum? The term peritoneum refers to the serous membrane that constitutes the biologically active inner... Read More
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (sER) is part of or a region in the endoplasmic... Read More
Lipogenesis
Lipogenesis Definition Lipogenesis is the process of producing lipid or fat to store biochemical energy for later metabolic... Read More
Sugar Homeostasis
Blood Sugar Regulation As described in Cell Biology tutorials, the body requires volumes of glucose in order to create ATP.... Read More
Carbohydrate
Carbohydrate Definition A biomolecule refers to any molecule that is produced by living organisms. As such, most of them... Read More
Parenchyma
Parenchyma Definition What does parenchyma mean? Let's define the word "parenchyma". Most of the functional tissues in... Read More
Polysaccharide
Polysaccharide Definition Biology Definition: A polysaccharide is a carbohydrate formed by long chains of repeating units... Read More
Clonorchis sinensis
Definition noun A liver fluke species belonging to the family Opisthorchiidae of the Class Trematoda, and endemic in Japan,... Read More
Perisinusoidal space
Definition noun The plasma-filled extravascular space in the liver, between a hepatocyte and a liver sinusoid Supplement The... Read More
Hepatocyte
Definition noun, plural: hepatocytes Any of the large, polygonal-shaped cells in the liver. Supplement Hepatocytes are the... Read More
Digestion and Absorption of Food
The gastrointestinal (GI) system includes the gastrointestinal tract (mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More
Erythrocyte
Erythrocyte Definition Erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs) are the myeloid series of specialized cells that play an... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
Saccharide
Saccharide Definition What is a saccharide molecule? A saccharide is the unit structure of carbohydrates. In biochemistry,... Read More
Cell differentiation
Cells are often described as the building blocks of life as they are the smallest unit used to build up organisms. Cells can... Read More
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the tendency not to stray from the range of favorable or ideal internal conditions. Such conditions must be... Read More
Fasciola hepatica
Definition noun A liver fluke belonging to the family Fasciolidae of the class Trematoda, and is endemic in the U.S.,... Read More
Assimilation
Assimilation Definition What is assimilation? Assimilation in biology is defined as the process in which living organisms... Read More
Regeneration in humans – Finding the gene switch
Regeneration in humans is much more limited compared in other animals. Say for instance when one lost a limb, much as well... Read More