Search Results for: lysis
Osmotic lysis
Definition noun The bursting or rupturing of cell membrane due to osmotic movement of water into the cell when the cell... Read More
Immune cytolysis
Definition noun (1) Cell lysis caused by a lesion produced by the complement proteins on the antibody-coated cell membrane... Read More
Plasmolysis
Plasmolysis is the shrinking of protoplasm away from the cell wall of a plant or bacterium. The protoplasmic shrinking is... Read More
Haemolysis
Definition noun The lysis or the breaking open of red blood cell (erythrocyte) causing the release of hemoglobin into the... Read More
Enzymolysis
Enzymolysis 1. The splitting or cleavage of a substance into smaller parts by means of enzymatic action. 2. Lysis by the... Read More
Hypotonic solution
Hypotonic Solution Definition What is a hypotonic solution? It refers to a solution that contains a lower amount of solute... Read More
Tendolysis
tendolysis release of a tendon from adhesions. Synonym: tenolysis. Origin: tendo-- G. Lysis,... Read More
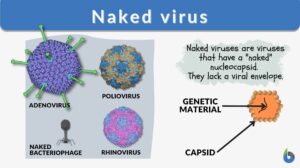
Naked virus
Viruses are infectious entities with size ranges between 20 to 400 nanometers. The mammoth-sized virus would be about the... Read More
Bacteriolysin
Definition noun, plural: bacteriolysins (1) A specific antibody that combines with bacterial cells (antigens) and, in the... Read More
Lytic cycle
Definition noun One of the two cycles of viral reproduction (the other being the lysogenic cycle), which is usually... Read More
Temperate virus
Definition noun A virus that does not cause immediate lysis following entry to its host but remains in a latent state,... Read More
Streptolysin O
Definition noun An oxygen-labile, immunogenic hemolysin produced by or derived from some strains of... Read More
Virulent virus
Definition noun A virus that lyses its host immediately upon infection and often cause disease Supplement Viruses may be... Read More
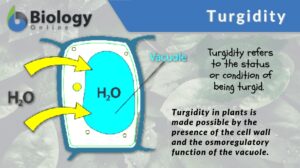
Turgor pressure
In biology, turgor pressure pertains to the pressure that is exerted by the fluid (e.g. water) against the cell wall. It is... Read More
Eubacteria
Eubacteria are prokaryotic microorganisms consisting of a single cell lacking a nucleus and containing DNA is a single... Read More
Saline solution
Saline Solution Definition Saline solution is one the most medically-used solution, which contains sodium chloride... Read More
Opsonization
Definition noun, plural: opsonizations The process at which opsonins bind to the surface of the antigen so that the... Read More
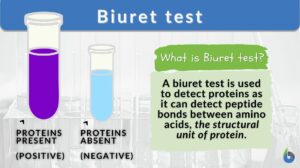
Biuret test
In this article we will answer the following three questions: What is a Biuret Test? What does biuret test for? What is... Read More
Plasma membrane
Do all cells have a plasma (or cell) membrane? Yes, all cells have a biological membrane that separates the protoplasm from... Read More
Elaioplast
Definition noun, plural: elaioplasts (botany) A leucoplast that stores oil Supplement Plastids are organelles involved in... Read More
Complement
Complement (Science: immunology) a term originally used to refer to the heat labile factor in serum that causes immune... Read More
Temperate phage
Definition noun, plural: temperate phages A bacteriophage that displays lysogenic life cycle in contrast to virulent phage... Read More
Bacteriophage
Definition noun, plural: bacteriophages A virus capable of infecting a bacterial cell, and may cause lysis to its host... Read More
Lysogenic conversion
Lysogenic conversion --> lysogeny (Science: virology) The ability of some phages to survive in a bacterium as a result of... Read More
Middle lamella
Definition noun plural: middle lamellae ˈmɪdəl ləˈmɛl.ə A pectin-rich intercellular material that glues the... Read More
Secondary cell wall
Definition noun plural: secondary cell walls ˈsɛkənˌdɛɹi sɛl wɔːl The layer of the plant cell wall that forms... Read More
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More