Search Results for: macrophage
Macrophage
Definition noun, plural: macrophages A leukocyte whose main function is to eliminate cellular debris and foreign particles... Read More
Wandering macrophage
wandering macrophage (Science: haematology) A macrophage that leaves the blood and migrates to infected... Read More
Permanent Tattoo Means Permanent Immune Action Of Macrophages
Have you ever wondered why a permanent tattoo seemed to last forever? A simple assumption would be is that the ink could... Read More
Endocytosis
Endocytosis Definition What is endocytosis in biology? Endocytosis is a cellular process by which a cell internalizes any... Read More
Histiocyte
Definition noun, plural: histiocytes A reticular connective tissue macrophage or a dendritic cell, derived from the bone... Read More
Myeloblast
Definition noun, plural: myeloblasts A precursor cell that gives rise to a promyelocyte during... Read More
Cell differentiation
Cells are often described as the building blocks of life as they are the smallest unit used to build up organisms. Cells can... Read More
Alveolar cell
Definition noun, plural: alveolar cells The cell lining the pulmonary alveolus; the cell of the air sac of the... Read More
Mononuclear phagocyte system
Definition noun A system of cells located in reticular connective tissue, and are associated primarily with phagocytosis and... Read More
Autocrine signaling
Autocrine Signaling Definition What is autocrine signaling? Autocrine signaling is a type of cell signaling wherein a cell... Read More
Kupffer cell
Definition noun, plural: Kupffer cells A specialized stellate macrophage cell that is located fixedly within the liver... Read More
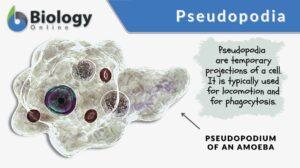
Pseudopodia
A pseudopodium (plural: pseudopodia) refers to the temporary projection of the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell. Pseudopodia... Read More
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis Definition Phagocytosis is a basic physiological cellular process wherein a cell ingests a solid particle... Read More
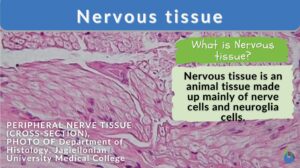
Nervous tissue
Nervous Tissue Definition Nerve cells (or neurons) and their associated cells, such as neuroglia cells, make up nervous... Read More
Exogenous pyrogen
Definition noun, plural: exogenous pyrogen A type of pyrogen that is of microbial origin, such as the lipopolysaccharide in... Read More
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that... Read More
Pinocytosis
Pinocytosis Definition What is pinocytosis? Pinocytosis is the ingestion of extracellular fluids, i.e. the fluid... Read More
Immunostimulator
Definition noun, plural: immunostimulators An agent capable of stimulating or increasing the activity of the immune... Read More
Autophosphorylation
Definition noun (biochemistry) The phosphorylation of the kinase through its own enzymatic... Read More
White blood cell
Definition noun, plural: white blood cells Any of the nucleated blood cells that lack hemoglobin, with a primary role in the... Read More
Langhans giant cell
Definition noun, plural: Langhans giant cells A type of giant cell formed by the fusion of epithelioid macrophages, and... Read More
Synovial membrane
Definition noun, plural: synovial joints The connective tissue lining the inner surface of the joint capsule of a synovial... Read More
Synovial joint
Definition noun A movable joint comprised of a layer of fibrocartilage or hyaline cartilage that lines the opposing bony... Read More
Joint capsule
Definition noun, plural: joint capsules A sac-like fibrous tissue that envelopes a synovial joint Supplement Synovial joints... Read More
Interferon
Interferon (Science: cytokine) a family of glycoproteins derived from human cells which normally has a role in fighting... Read More
Biological Cell Defense
Organisms must find a means of defense against antigens such a viruses described on the previous tutorial. If this was not... Read More
Plasma membrane
Do all cells have a plasma (or cell) membrane? Yes, all cells have a biological membrane that separates the protoplasm from... Read More