Search Results for: molecule
Biomolecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral, group of atoms that can exist alone in a free state while its characteristic... Read More
Micromolecule
Micromolecules Definition How to define micromolecule? Micromolecules are relatively small molecules that are combined... Read More
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that... Read More
Inorganic molecule
Definition noun, plural: inorganic molecules (1) A molecule not consisting of carbon atoms. (2) Any molecule that is not... Read More
Polar molecule
Definition noun, plural: polar molecules A molecule with a net dipole as a result of the opposing charges (i.e. having... Read More
Movement of Molecules Across Cell Membranes
Diffusion Diffusion is essentially the movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower... Read More
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
Plant Metabolism
Introduction Plants are responsible for incredible feats of molecular transformation. The processes are always being... Read More
Organic molecule
Definition noun 1. A molecule that is normally found in or produced by living systems. 2. A molecule that typically... Read More
Dehydration reaction
What is dehydration synthesis? A dehydration reaction is a form of biochemical reaction wherein a water molecule is lost or... Read More
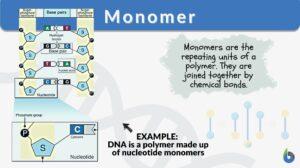
Nucleic acid
Nucleic Acid Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds consisting of chains of monomers of... Read More
Hydrophilic
Hydrophilic Definition What does a hydrophile (or hydrophilic molecule) mean? If a molecule is “water-loving”, it is... Read More
Chemical Composition of the Body
In order to fully understand the mechanisms of human physiology, it is important to have an understanding of the chemical... Read More
Light-dependent reaction
Many organisms, such as green plants, convert light energy into chemical energy through the mechanism of photosynthesis. In... Read More
Calvin cycle
Calvin Cycle Definition The Calvin cycle, also known as the Calvin Benson cycle or the dark reactions, is a series of... Read More
Genetic Information and Protein Synthesis
Genetic Code Genes are sequences of DNA nucleotides that carry and transmit the information specifying amino acid sequences... Read More
Hydrogen bond
Definition noun plural: hydrogen bonds A type of chemical bond that is formed when the slightly positive hydrogen atom of... Read More
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation Definition We can define phosphorylation as a biochemical process in which a phosphate molecule is added to... Read More
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physio-chemical process carried out by photo-auto-lithotrophs by converting light energy into chemical... Read More
Protein Activity and Cellular Metabolism
Protein Binding Sites The ability of various molecules and ions to bind to specific sites on the protein surface forms the... Read More
Fermentation
Fermentation Definition What is fermentation? Fermentation is the breaking down of sugar molecules into simpler compounds... Read More
Photolysis
Photolysis Definition We define photolysis as a chemical process in which chemical compounds or molecules are split into... Read More
Covalent bond
Covalent Bond Definition What is a covalent bond? In chemistry and other fundamental science fields, a covalent bond is... Read More
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
Macromolecule
Definition noun, plural: macromolecules A large complex molecule, such as nucleic acids, proteins, carbohydrates, and... Read More
Phospholipid
What is a phospholipid? Phospholipids are a subgroup of lipids. Other major types of lipids are fatty acids, sphingolipids,... Read More
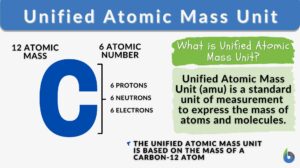
Unified atomic mass unit
Unified Atomic Mass Unit Definition The Unified Atomic Mass Unit (u) (or simply atomic mass unit) refers to the 1/12... Read More
Chlorophyll
Why are most plants green? Have you ever had the same question? Perhaps, you’ve been told that the plants are green... Read More
Hydrophobic
Hydrophobic Definition The fear of mixing or reacting with water under a given set of reaction parameters is often referred... Read More
Anaerobic respiration
Anaerobic Respiration Definition What is anaerobic respiration? Anaerobic (cellular) respiration is a respiratory process... Read More