Search Results for: multiply
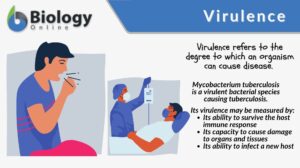
Multiplication
multiplication 1. The act or process of multiplying, or of increasing in number; the state of being multiplied; as, the... Read More
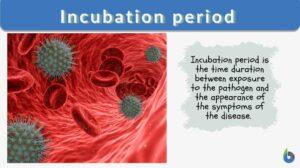
Incubation period
Incubation Period Definition The incubation period is the time duration between exposure to the pathogen and the appearance... Read More
Thermometer
thermometer (Science: physics) An instrument for measuring temperature, founded on the principle that changes of temperature... Read More
Tachyzoite
Definition noun, plural: tachyzoites A relatively faster-growing, actively multiplying, and invasive cell type of certain... Read More
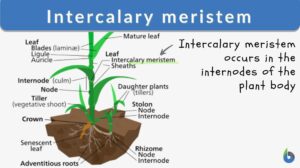
Intercalary meristem
The basic structural framework of plants is composed of different types of tissues. Based upon the capacity to divide, the... Read More
Dumdum fever
Dumdum fever --> visceral leishmaniasis a chronic disease, occurring in india, Assam, china, the area formerly known as... Read More
Cell differentiation
Cells are often described as the building blocks of life as they are the smallest unit used to build up organisms. Cells can... Read More
Black sickness
Black sickness --> visceral leishmaniasis a chronic disease, occurring in india, Assam, china, the area formerly known as... Read More
Prokaryote
Prokaryote refers to any of the group of living organisms primarily characterized by the lack of a true nucleus and other... Read More
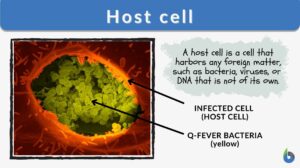
Amplifier host
Amplifier host a host in which infectious agents multiply rapidly to high levels, providing an important source of infection... Read More
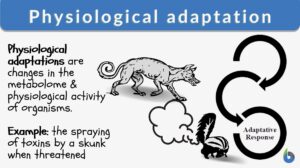
Physiological adaptation
If we look over evolutionary history, we find that it’s neither the most genius and intelligent nor the strongest and the... Read More
Cytokinesis
The cell cycle of eukaryotes is a cyclical series of biological events that certain asexual cells go through. The cell cycle... Read More
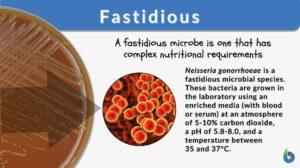
Fastidious
Fastidious Definition We can define fastidious as a term used in microbiology to denote a species that lacks the ability to... Read More
Microparasites
Microparasites (Science: epidemiology) Typically, viruses, bacteria, fungi and protozoa. More generally, parasites that... Read More
Carbon fixation
Carbon Fixation Definition We know that the earth contains many elements. The periodic table shows us just how many... Read More
Cell adhesion
Cell Adhesion Definition Cell adhesion is the process in which a cell uses a specialized complex of proteins to get... Read More
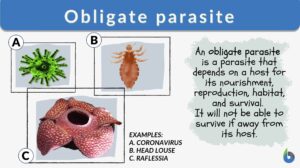
Obligate parasite
Parasitism is a form of symbiosis that occurs between a parasite and its host. The parasite is the organism that generally... Read More
Lymph nodes
Lymph nodes definition Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped organs located in different parts of the body and act as... Read More
Breathing rate
Breathing rate (Science: chest medicine, clinical sign) also referred to as the respiratory rate. Measured as the number of... Read More
Digestion and Absorption of Food
The gastrointestinal (GI) system includes the gastrointestinal tract (mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,... Read More