Search Results for: nucleus
Micronucleus
Definition noun, plural: micronuclei The small type of nucleus in ciliates, and is responsible for cell division in... Read More
Rollers nucleus
Roller's nucleus lateral nucleus of the accessory nerve, a small bulbar nucleus lying immediately anterior to the... Read More
Hypothalamus
Definition noun, plural: hypothalami A small region of the forebrain comprised of several small nuclei, located between the... Read More
Macronucleus
Definition noun, plural: macronuclei The larger type of nucleus involved in non-reproductive functions (as opposed to the... Read More
Eukaryotic cells
Eukaryotic Cells Definition What is a eukaryotic cell? Eukaryotic cells refer to the cells of (or derived from) eukaryotes,... Read More
Endomembrane system
Ever wondered how biomolecules are made within the cell and then they are released outside the cell for use by the body?... Read More
Nuclear envelope
Definition noun plural: nuclear envelopes nu·cle·ar en·ve·lope, ˈn(j)ukliɚ ˈɛn.və.ləʊp The two layered membrane... Read More
Prokaryote
Prokaryote refers to any of the group of living organisms primarily characterized by the lack of a true nucleus and other... Read More
Plant Cells vs. Animal Cells
Plant Cells Most cells are not visible with the naked eye. However, with microscopes of various types, plant cells can be... Read More
Actions of Caffeine in the Brain with Special Reference to Factors That Contribute to Its Widespread Use
IV. Actions of Caffeine on Brain Functions and BehaviorHaving discussed the molecular and neuronal actions of caffeine,... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
Nucleoplasm
Definition noun plural: nucleoplasm nu·cle·o·plasm, ˈnjuːklɪəˌplæzəm (cell biology) The protoplasm of the... Read More
Cell Structure
The interior of human cells is divided into the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The nucleus is a spherical or oval-shaped... Read More
Pronucleus
pronucleus (Science: molecular biology) haploid nucleus resulting from meiosis. In animals the female pronucleus is the... Read More
Nuclear pore complex
Definition noun plural: nuclear pore complexes ˈnu kli ər, pɔː ˈkɒmplɛks A complex of nucleoporins resulting in the... Read More
Nuclear pore
Definition noun plural: nuclear pores ˈnu kli ər, pɔː Any of the many perforations on the nucleus as a result of the... Read More
Chromosome
Chromosomes Definition Chromosomes are thread-like structures present in the nucleus of plant and animal cells. Chromosomes... Read More
Nuclear matrix
Definition noun plural: nuclear matrices (cell biology) A 3-dimensional filamentous protein network that extends... Read More
Nuclear body
Definition noun plural: nuclear bodies nu·cle·ar bod‧y, ˈnjuː.kli.ər ˈbɒdi Any of the prominent non-membraned,... Read More
Nucleoporin
Definition noun plural: nucleoporins Any of the family of porins that make up the nuclear pore complex Details Overview... Read More
Cytokinesis
The cell cycle of eukaryotes is a cyclical series of biological events that certain asexual cells go through. The cell cycle... Read More
Deoxyribonucleic acid
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds made up of linear... Read More
Nuclear lamina
Definition noun plural: nuclear laminae or nuclear laminas nu·cle·ar lam·i·na, ˈn(j)ukliɚ ˈlæm.ɪ.nə (cell... Read More
Eubacteria
Eubacteria are prokaryotic microorganisms consisting of a single cell lacking a nucleus and containing DNA is a single... Read More
Nucleic acid
Nucleic Acid Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds consisting of chains of monomers of... Read More
Bondok’s Classification of the Thalamic Nuclei
Anatomists usually classify the thalamic nuclei according to their relation to the internal medullary lamina into 5 groups:... Read More
Nucleosome
Nucleosome Definition Every organism is made of deoxyribonucleic acid, also known as DNA. DNA is made up of numerous... Read More
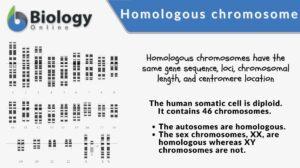
Homologous chromosome
A homologous chromosome pertains to one of a pair of chromosomes with the same gene sequence, loci, chromosomal length, and... Read More