Search Results for: phosphoenolpyruvate
Phosphoenolpyruvate
phosphoenolpyruvate (Science: biochemistry) An important metabolic intermediate. The enol (less stable) form of pyruvic acid... Read More
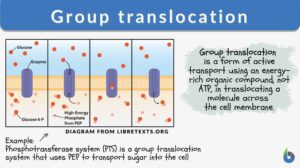
Group translocation
Group Translocation Definition Just like your “home” is a private place where you and your comfort are maintained due... Read More
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
PEP carboxylase
Definition noun An enzyme in the carboxylases responsible for the formation of the four-carbon compound oxaloacetate by... Read More
Hatch-Slack pathway
Definition noun A metabolic pathway first delineated in depth by M. D. Hatch and C. R. Slack (in 1966). In this pathway, the... Read More
C4 carbon fixation pathway
Definition noun A metabolic pathway where CO2 is first added to phosphoenolpyruvate by the enzyme, PEP carboxylase,... Read More
Hsk pathway
Definition noun An abbreviation for hatch slack kortshak pathway: a metabolic pathway first determined by Burr and Kortshak... Read More
Pyruvic acid
What is Pyruvic Acid? Pyruvic acid is an organic acid that occurs as an intermediate in many metabolic processes. It occurs... Read More
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physio-chemical process carried out by photo-auto-lithotrophs by converting light energy into chemical... Read More
Guanosine diphosphate
Definition noun plural: guanosine diphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide made up of guanine, ribose, and two phosphate... Read More
Plant Metabolism
Introduction Plants are responsible for incredible feats of molecular transformation. The processes are always being... Read More