Search Results for: precursor
Precursor mRNA
Definition noun plural: precursor mRNAs An immature or incompletely processed mRNA molecule in eukaryotes that needs to be... Read More
Mature mRNA
Mature mRNA Definition Mature mRNA is the completely processed mRNA molecule in the cell of eukaryotes. The mRNA is a type... Read More
Myeloblast
Definition noun, plural: myeloblasts A precursor cell that gives rise to a promyelocyte during... Read More
Promegakaryocyte
Definition noun, plural: promegakayocytes A precursor cell in the thrombocytic series that arises from a megakaryoblast and... Read More
Lipotropin
Definition noun, plural: lipotropins A polypeptide hormone of the anterior pituitary gland, presumably acts by promoting fat... Read More
Differentiation
Differentiation in biology is the process where less specialized cells undergo changes to develop specialized structures and... Read More
Zymogen granules
Definition noun The granules in the cytoplasm of secretory cells containing the zymogen Supplement Zymogen granules are... Read More
Megakaryocyte
Definition noun, plural: megakaryocytes A large cell in the bone marrow with characteristic lobulate nucleus and is... Read More
Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D.Eukaryotic Gene Structure In prokaryotes the DNA is located in the... Read More
Chemosynthesis
Definition noun, plural: chemosyntheses The production of a more complex chemical compound by combining two or more simpler... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
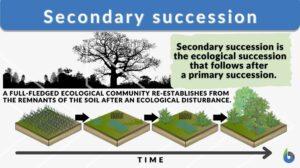
Secondary succession
We all have come across news where forest lands got destroyed by wildfires. Or sometimes we have read about an entire... Read More
Enzyme activation
Enzyme activation conversion of an inactive form of an enzyme to one possessing metabolic activity. It includes 1)... Read More
Deoxythymidine
Definition noun plural: deoxythymidines A pyrimidine nucleoside that has thymine attached to the pentose sugar... Read More
Erythroblast
Definition noun, plural: erythroblasts A nucleated red blood cell that develops into a reticulocyte Supplement The blood... Read More
De novo pathway
Definition noun, plural: de novo pathways (biochemistry) A biochemical pathway where a complex biomolecule is synthesized... Read More
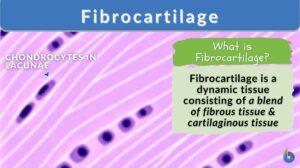
Fibrocartilage
What Is Fibrocartilage? Fibrocartilage is the strongest transitional connective tissue made up of collagen fibers and... Read More
Angiotensinogen
Definition noun An alpha-2 globulin protein that is found in the bloodstream and release into circulation mainly by the... Read More
Megakaryoblast
Definition noun, plural: megakaryoblasts A precursor cell that develops into a promegakaryocyte during... Read More
Thyrotroph
Definition noun, plural: thyrotrophs The cell in the anterior pituitary that particularly releases thyroid-stimulating... Read More
First time! Human blood cell turned into a young sex cell
In essence, our body consists of two major types of cells – one group involved directly in reproducing sexually (called... Read More
Genetic Control – On and Off Genes
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D.This lesson looks at the various factors involved that affect growth and... Read More
Digestion and Absorption of Food
The gastrointestinal (GI) system includes the gastrointestinal tract (mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More
Principles of Hormonal Control Systems
Hormones are chemical messengers that enter the blood directly upon their secretion from endocrine glands. A single gland or... Read More
Mononucleotide
Definition noun plural: mononucleotides mon·o·nu·cle·o·tide, ˌmɒnəʊˈnjuːklɪəˌtaɪd A single nucleotide (as... Read More
Uridine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: uridine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of uracil, ribose and a phosphate... Read More