Search Results for: radioactive
Radioactive atom
Radioactive atom (Science: chemistry, physics) An atom with an unstable nucleus, which emits particulate or electromagnetic... Read More
Radioactive decay
radioactive decay (Science: physics) The process by which a spontaneous change in nuclear state takes place. This process is... Read More
Contamination
Contamination Definition Contamination, sometimes interchanged with pollution, is the existence of live things or... Read More
Radioactive
radioactive Giving off... Read More
First-order kinetics
What is a First-Order Kinetics (First-Order Reaction)? First-order kinetics refers to a reaction wherein the overall rate... Read More
Irradiation
Irradiation treatment by ionising radiation, such as x-rays or radioactive sources such as radioactive iodine seeds. See:... Read More
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physio-chemical process carried out by photo-auto-lithotrophs by converting light energy into chemical... Read More
Maxam-Gilbert sequencing
Definition noun A DNA sequencing technique developed in 1976-1977 by Allan Maxam and Walter Gilbart to identify the sequence... Read More
Secular equilibrium
secular equilibrium A type of radioactive equilibrium in which the half-life of the precursor (parent) radioisotope is so... Read More
Activation
Definition noun (general) The state or the process of being active and/or effective (biochemistry) The process of making a... Read More
Metabolism
Metabolism Definition What is metabolism in the body? Metabolism encompasses the various biochemical processes, reactions,... Read More
Prokaryote
Prokaryote refers to any of the group of living organisms primarily characterized by the lack of a true nucleus and other... Read More
Dna ligase
Dna ligase (Science: enzyme molecular biology) enzyme involved in dna replication. The dna ligase of E. Coli seals nicks in... Read More
Calvin cycle
Calvin Cycle Definition The Calvin cycle, also known as the Calvin Benson cycle or the dark reactions, is a series of... Read More
Disintegration
Disintegration The process by which anything is disintegrated; the condition of anything which is disintegrated. (Science:... Read More
Peroxidase
peroxidase (Science: enzyme) A haem enzyme that catalyses reduction of hydrogen peroxide by a substrate that loses two... Read More
Pioneer species
You might have come across news of some barren lands turning into luscious grasslands or forests after decades? Or you might... Read More
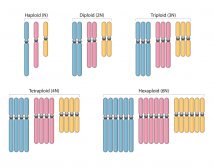
Polyploidy
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D.Polyploidy Polyploidy is defined as the state of being polyploid, which... Read More