Search Results for: replicate
HSV-2- and HIV-1- permissive cell lines co-infected by HSV-2 and HIV-1 co-replicate HSV-2 and HIV-1 without production of HSV-2/HIV-1 pseudotype particles
Jérôme LeGoff1, Hicham Bouhlal1, Maxime Lecerf1, Christophe Klein2, Hakim Hocini1, Ali Si-Mohamed1, Martin Muggeridge3 and... Read More
Triplicate
Definition noun, plural: triplicates One of the three identical copies or replicates verb To make three copies... Read More
Centrosome
Centrosome Definition What is a centrosome? The centrosome is considered to be the main microtubule-organizing... Read More
Biological Cell Defense
Organisms must find a means of defense against antigens such a viruses described on the previous tutorial. If this was not... Read More
Biological Viruses
The prime directive of all organisms is to reproduce and survive and this also applies to viruses. Apparently, viruses are... Read More
Conditional-lethal mutant
Conditional-lethal mutant --> conditionally lethal mutant a viral mutant that can replicate under some (permissive)... Read More
Eubacteria
Eubacteria are prokaryotic microorganisms consisting of a single cell lacking a nucleus and containing DNA is a single... Read More
Genetic material
Genetic Material Definition What is genetic material? Genetic material is the hereditary substance in the cell. It carries... Read More
Reservoir host
Reservoir Host Definition A reservoir host is a host that harbors the pathogen and serves as a source of the infective... Read More
Living things
Living Things Definition A living thing pertains to any organism or a life form that possesses or shows the characteristics... Read More
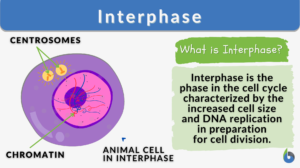
Interphase
Interphase is the critical period in the eukaryotic cell cycle characterized by a sequence of events like the G1 phase where... Read More
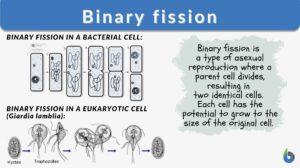
Binary fission
Binary Fission Definition What is binary fission? In biology, binary fission is a type of asexual reproduction where a... Read More
Nucleic acid
Nucleic Acid Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds consisting of chains of monomers of... Read More
Meiosis and Alternation of Generations
Review of Mitosis: Cell Cycle The cell cycle contains the process in which cells are either dividing or in between... Read More
Cell division
Cell division is a biological process by which a parent cell duplicates its cell contents and divides to give rise to two or... Read More
Single-stranded DNA
What is single-stranded DNA? DNA is the material that living organisms possess that carries their genetic make-up. DNA and... Read More
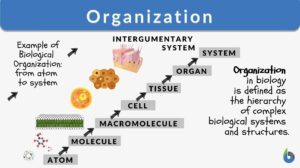
Organization
Organization Definition The meaning of the term "organization" is very simple. It means the state wherein things are... Read More
Fluctuation test
Fluctuation test (Science: investigation) test devised by Luria and Delbruck to determine whether genetic variation in a... Read More
Genetic Engineering Advantages & Disadvantages
Through genetic engineering, scientists are able to move desirable genes from one plant or animal to another or... Read More
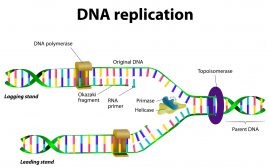
DNA Structure & DNA Replication
Previous pages in this tutorial have described the basics of a cell, the energy required by these cells and how energy is... Read More
Protein Synthesis
If you have jumped straight to this page, you may wish to look at the previous tutorial about DNA, which gives background... Read More
Biochemical Genetics
Definition noun A branch of genetics at a biochemical level and in which the relationship of genes and their control over... Read More
Double stranded DNA virus
Definition noun Any of the viruses belonging to the Class I of Baltimore classification system characterized by having a... Read More
Transposon
Definition noun, plural: transposons A small segment of DNA that is capable of replicating and inserting copies of DNA at... Read More
Single stranded DNA virus
Definition noun Any of the viruses belonging to the Class II of Baltimore classification system characterized by having a... Read More
Prodromal period
There are five stages (or phases) of a disease. (Hattis, 2020). These stages are (1) Incubation period, (2) Prodromal... Read More
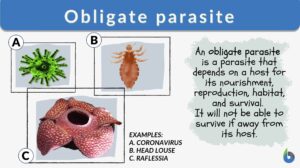
Obligate parasite
Parasitism is a form of symbiosis that occurs between a parasite and its host. The parasite is the organism that generally... Read More
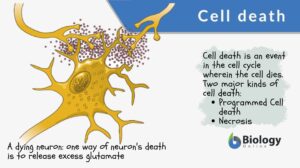
Cell death
Cell Death Definition Cell death refers to the event that leads to the death of a cell. The process entails the breaking... Read More
Kelp Forest
Definition noun, The most biologically productive habitat found in the cold rich nutrient marine ecosystem. Supplement The... Read More
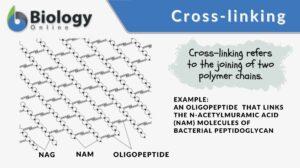
Cross-linking
Cross-linking Definition Cross-linking, in general, means the forming of cross-links between the joining structures. In... Read More
Shuttle vector
Definition noun A vector that can replicate in more than one host organisms or two different cell types (e.g. a prokaryotic... Read More