Search Results for: retina
Tigroid retina
tigroid retina --> tessellated fundus A normal fundus to which a deeply pigmented choroid gives the appearance of dark... Read More
Pupillary light reflex
Definition noun, plural: pupillary light reflexes A reflex marked by the constriction of the pupil in response to the... Read More
Human Perception – Neurology
A better understanding of human perception unlocks the key to how the mind works, an advantage when working with people with... Read More
Tapetum lucidum
Definition noun, plural: tapeta lucida A layer of tissue in the choroid or in the retinal pigment epithelium of the eye of... Read More
Sensory Systems
A sensory system is a part of the nervous system consisting of sensory receptors that receive stimuli from the internal and... Read More
Young-helmholtz theory of colour vision
'''Young-helmholtz theory of color vision A theory that there are three perceiving elements in the retina: red, green, and... Read More
Sclerotome
Definition noun, plural: sclerotomes (embryology) The somite that gives rise to the development of vertebrae and... Read More
Wagners syndrome
Definition noun (1) A degenerative condition of the vitreous and retinal parts of the eye, and may eventually lead to... Read More
Vitreous humor
Definition noun The clear, gel-like body fluid in the vitreous chamber, i.e. the posterior cavity between the lens and the... Read More
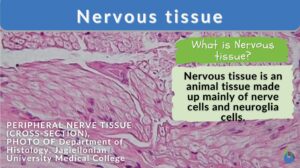
Nervous tissue
Nervous Tissue Definition Nerve cells (or neurons) and their associated cells, such as neuroglia cells, make up nervous... Read More
Sense organ
Definition noun, plural: sense organs An organ or structure that has nerve endings capable of detecting and reacting to a... Read More
Punctum caecum
Definition noun A region in the retina that does not contain photoreceptors thus leads to the normal blind spot in the... Read More
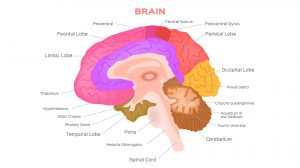
Nervous System
THE is the most complicated and highly organized of the various systems which make up the human body. It is the... Read More
Accommodation reflex
Definition noun, plural: accommodation reflexes A reflex reaction of the eye in response to focusing on near object followed... Read More
Macula lutea
Macula lutea An oval area in the retina, 3 to 5 mm in diameter, usually located temporal to the posterior pole of the eye... Read More
Human Neurology
Human Neurology deals essentially with the nervous system of humans. It also features the various theories put forward by... Read More
Neurology of Illusions
As mentioned in the previous tutorial, Human Perception, illusions can be caused by mental disorders or misreading of the... Read More
Blindness – Evolutionary regression? Maybe not!
The recent Netflix's hit flick, Bird Box, surely startled the viewers with the thrilling scenarios revolving around the... Read More
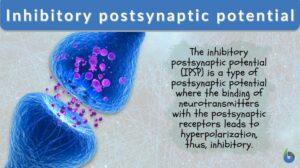
Inhibitory postsynaptic potential
Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential Definition An inhibitory postsynaptic potential is a type of synaptic potential. It is... Read More
Hyaloid canal
Hyaloid canal a minute canal running through the vitreous from the discus nervi optici to the lens, containing in foetal... Read More
Undulatory
undulatory moving in the manner of undulations, or waves; resembling the motion of waves, which successively rise or swell... Read More
Quadrantanopia
Definition noun, plural: quadrantanopias A visual field defect characterized by a loss of vision in a quarter section of the... Read More
Hypermetropia
Hypermetropia --> hyperopia farsightedness or hyperopia occurs when a refractive error in which light rays entering the... Read More
Electrical synapse
Definition noun A form of synapse between two apposed neurons in which nerve impulse transmission is rapid and occurs by... Read More
Punctum proximum
punctum proximum --> near point That point in conjugate focus with the retina when the eye exerts maximal... Read More