Search Results for: sheep
Interspecific competition
Interspecific Competition Definition In Biology, competition is defined as the process that occurs among species that have... Read More
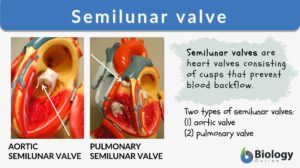
Semilunar valve
The human heart structure consists of heart chambers (2 atria and 2 ventricles) that differ functionally from each other.... Read More
New Zealand’s Unique Flora
By: Maria Victoria GonzagaIn the previous lesson, we've come to know some of the most fascinating endemic... Read More
Homogenous
What is homogenous? What does homogenous mean? The word homogenous has been derived from two Greek words that are... Read More
Visna maedi virus
Visna maedi virus (Science: virology) A retrovirus of sheep and goats. A member of the lentivirus subfamily related to... Read More
Complement fixation test
Definition noun (immunology) A form of immunological test for the detection of the presence of either a particular antibody... Read More
Fasciola hepatica
Definition noun A liver fluke belonging to the family Fasciolidae of the class Trematoda, and is endemic in the U.S.,... Read More
Alimentary canal
Definition of Alimentary canal What is the alimentary canal? The alimentary canal is a muscular hollow continuous tubular... Read More
Genetic Engineering Advantages & Disadvantages
Through genetic engineering, scientists are able to move desirable genes from one plant or animal to another or... Read More
Hydrous wool fat
Hydrous wool fat --> adeps lanae The greasy substance obtained from the wool of the sheep Ovis aries (family Bovidae). Used... Read More
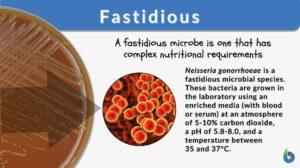
Fastidious
Fastidious Definition We can define fastidious as a term used in microbiology to denote a species that lacks the ability to... Read More
Carbohydrate
Carbohydrate Definition A biomolecule refers to any molecule that is produced by living organisms. As such, most of them... Read More
Biotic factor
Biotic Factor Definition A biotic factor is the living component in an ecosystem. The term "biotic" means "of or related... Read More
Lamarckism
Definition noun The theory suggesting that traits or characteristics of an organism are produced and inherited by direct... Read More
SENI Biometric Analysis on the extinct Scincidae species: Macroscincus coctei (underlined)
Brian L. Schnirel Leeway Corucia Research Center (LCRC) Courtesy: Polyphemos (2004) Introduction: It has been... Read More
Lamarckian theory
Definition noun An evolutionary theory holding that acquired or learned traits can be passed on from parents to... Read More
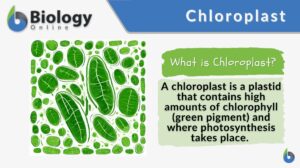
Chloroplast
Chloroplast Definition What is chloroplast? In biology, a chloroplast refers to the organelle found within the cell of... Read More
White adipose tissue
Definition noun, plural: white adipose tissues A type of adipose tissue found in mammals used to store energy and acts as... Read More