Search Results for: soil
Soil Science & Management (4th Ed) by E. Plaster
Soil Science & Management ... Read More
Soil percolation
soil percolation describes the process by which a material more fluid than soil, usually water, moves through soil refers to... Read More
Soil horizon
Soil horizon A distinct layer of soil, more or less parallel with the soil surface, having similar properties such as... Read More
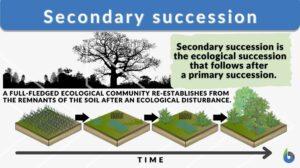
Secondary succession
We all have come across news where forest lands got destroyed by wildfires. Or sometimes we have read about an entire... Read More
Decomposer
Decomposer Definition The organisms that carry out the process of decay or breakdown of the dead organism are known as... Read More
Poorly drained soil
poorly drained soil (Science: ecology) A condition in which water is removed form the soil so slowly that the soil is... Read More
Saturated soil
saturated soil A condition in which all easily drained voids (pores) between soil particles are temporarily or permanently... Read More
Mineral soil
mineral soil (Science: ecology) Any soil consisting primarily of mineral (sand, silt and clay) material, rather than organic... Read More
Soil microbiology
soil microbiology The presence of bacteria, viruses, and fungi in the soil. This term is not restricted to pathogenic... Read More
Abiotic factor
An abiotic factor is a non-living element of the environment that influences the way organisms and ecosystems function. Some... Read More
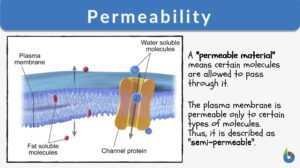
Permeability
Permeability Definition What is permeability? In earth science, its definition is this: "the ability of any material such... Read More
Organic matter
Definition noun Any of the carbon-based compounds found in nature Supplement Organic matter pertains to any of the... Read More
Ecosystem Succession
Just one of the amazing aspects of life on Earth is that it spreads to all areas where the habitat will allow it to survive.... Read More
Recalcitrant
Several words of the English language find wide usage in subjects as diverse as literature, science, social science,... Read More
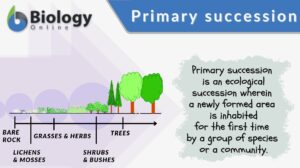
Primary succession
Primary Succession Definition Primary succession is an ecological succession where a newly formed area is inhabited for the... Read More
Vascular plants
Definition of Vascular plants The term 'vascular' is derived from the Latin word vāsculum, vās, meaning "a container and... Read More
Pneumatophore
Definition noun, plural: pneumatophores (botany) A specialized aerial root, such as in certain mangrove species, that stick... Read More
Water in Plants
The movement of molecules, specifically water and any solutes, is vital to understand in light of plant processes. This will... Read More
Pioneer species
You might have come across news of some barren lands turning into luscious grasslands or forests after decades? Or you might... Read More
Cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria Definition Cyanobacteria is a group of photosynthetic bacteria widely distributed in various aquatic habitats... Read More
Unicellular
Unicellular organisms are organisms consisting of one cell only that performs all vital functions including metabolism,... Read More
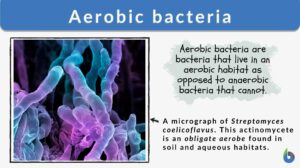
Aerobic bacteria
Aerobic Bacteria Definition What does aerobic mean in biology? As the name suggests, 'aerobe' in biology means organisms... Read More
Angiosperm
Angiosperms Definition What is an angiosperm? An angiosperm is a plant that produces flowers. The angiosperms, also... Read More
Hypertonic
Hypertonic Definition Hypertonic is a term used to describe an entity being in the state of hypertonicity, where there is a... Read More