Search Results for: specificity
Sensitivity and specificity
Definition noun Statistical measures for assessing the results of diagnostics and screening tests wherein sensitivity... Read More
Substrate specificity
Definition noun A feature of enzyme activity with regard to the kind of substrate reacting with an enzyme to yield a... Read More
Specificity
specificity The ability of the immune response to interact with individual... Read More
Stereospecificity
Definition noun Relate to the specific points along the chain of configurations resulting in the spatial arrangement of... Read More
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation Definition We can define phosphorylation as a biochemical process in which a phosphate molecule is added to... Read More
Protein Activity and Cellular Metabolism
Protein Binding Sites The ability of various molecules and ions to bind to specific sites on the protein surface forms the... Read More
Tight junction
What are tight junctions? Tight junctions are the intercellular barrier between two neighboring endothelial and epithelial... Read More
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis Definition Phagocytosis is a basic physiological cellular process wherein a cell ingests a solid particle... Read More
Sensory Systems
A sensory system is a part of the nervous system consisting of sensory receptors that receive stimuli from the internal and... Read More
Radial immunodiffusion
Definition noun A quantitative immunodiffusion technique used to detect the level of protein (antigen) in a sample by... Read More
Between Necessity and Probability: Searching for the Definition and Origin of Life (Advances in Astrobiology and Biogeophysics)
Between Necessity and Probability: Searching for the Definition and Origin of Life (Advances in Astrobiology and... Read More
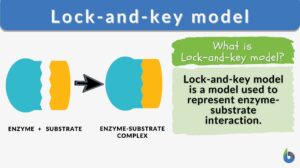
Lock-and-key model
Lock-and-key model Definition Lock-and-key model is a model for enzyme-substrate interaction suggesting that the enzyme and... Read More
Silent mutation
A mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene or a chromosome. When there is only one nucleotide involved, it... Read More
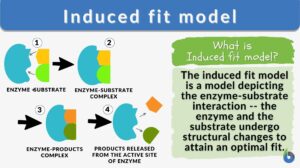
Induced fit model
Induced-Fit Model Definition The induced-fit model is a model for enzyme-substrate interaction to depict the dynamic... Read More
Codominance
Codominance Definition Codominance is a form of inheritance wherein the alleles of a gene pair in a heterozygote are fully... Read More
Cell differentiation
Cells are often described as the building blocks of life as they are the smallest unit used to build up organisms. Cells can... Read More
Tissue distribution
tissue distribution accumulation of a drug or chemical substance in various organs (including those not relevant to its... Read More
Phospholipid
What is a phospholipid? Phospholipids are a subgroup of lipids. Other major types of lipids are fatty acids, sphingolipids,... Read More
Cell theory
What Is Cell Theory? Biological cell theory explains the idea of organismal constitution, structure, and function. It... Read More
Eubacteria
Eubacteria are prokaryotic microorganisms consisting of a single cell lacking a nucleus and containing DNA is a single... Read More
Phosphatase
phosphatase (Science: enzyme) That hydrolyse phosphomonoesters. Acid phosphatases are specific for the single charged... Read More
Gelatinase
Definition noun, plural: gelatinases (1) Pepsin B derived from pepsinogen B. It is similar to pepsin A but with more... Read More
Cell adhesion
Cell Adhesion Definition Cell adhesion is the process in which a cell uses a specialized complex of proteins to get... Read More
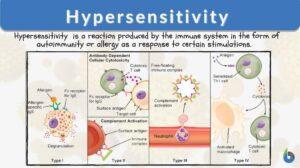
Hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity Definition Hypersensitivity is the exaggerated immune response to protect the human from foreign bodies... Read More
Human milk oligosaccharide
Definition noun plural: human milk oligosaccharides An oligosaccharide that occurs in high concentrations and exclusively... Read More