Search Results for: storage
Parenchyma
Parenchyma Definition What does parenchyma mean? Let's define the word "parenchyma". Most of the functional tissues in... Read More
Storage granule
storage granule 1. (Science: cell biology) membrane bounded vesicles containing condensed secretory materials (often in an... Read More
Metabolism
Metabolism Definition What is metabolism in the body? Metabolism encompasses the various biochemical processes, reactions,... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
Polysaccharide
Polysaccharide Definition Biology Definition: A polysaccharide is a carbohydrate formed by long chains of repeating units... Read More
Lipogenesis
Lipogenesis Definition Lipogenesis is the process of producing lipid or fat to store biochemical energy for later metabolic... Read More
Elaioplast
Definition noun, plural: elaioplasts (botany) A leucoplast that stores oil Supplement Plastids are organelles involved in... Read More
Herring body
Definition noun, plural: Herring bodies The neurosecretory terminal of the axons from the hypothalamus and located in the... Read More
Amyloplast
Definition noun, plural: amyloplasts (botany) A type of leucoplast found in the cytoplasm of a plant cell, and serves as... Read More
Austin disease
Definition noun A type of lysosomal storage disease that is often caused by a deficiency in multiple sulfatase enzymes, or... Read More
Glycogenosis
Definition noun, plural: glycogenoses A metabolic disorder caused by a defective glycogen metabolism resulting in the extra... Read More
Adipose tissue
Adipose Tissue Definition Adipose tissue, a specialized variety of connective tissue, is composed of lipid-rich cells known... Read More
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (sER) is part of or a region in the endoplasmic... Read More
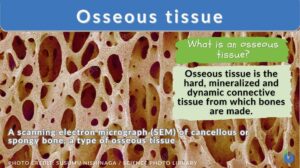
Osseous tissue
What Is Bone Or Osseous Tissue? Osseous tissue is the structure providing, hard and mineralized connective tissues. Osseous... Read More
Leucoplast
Definition noun, plural: leucoplasts A plastid lacking photosynthetic pigments and involved in various biosynthetic... Read More
Oligosaccharide
Carbohydrates are organic compounds consisting of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, usually in the ratio of 1:2:1. They are one... Read More
Lysosomal enzyme
Definition noun plural: lysosomal enzymes ly·so·somal en·zyme, ˈlaɪsəˌsoʊm əl ˈɛnzaɪm (biochemistry) Any of... Read More
Endomembrane system
Ever wondered how biomolecules are made within the cell and then they are released outside the cell for use by the body?... Read More
Mucolipidosis
Definition noun A type of mucopolysaccharides and mucolipids Supplement Lysosomal storage disease is a collective term for... Read More