Search Results for: tyrosine
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation Definition We can define phosphorylation as a biochemical process in which a phosphate molecule is added to... Read More
Millons test
Definition noun A color reaction test using Millon's reagent to detect phenolic compounds (e.g. tyrosine) Supplement French... Read More
Melanogenesis
Definition noun The process of producing melanin Supplement Melanogenesis is the process of melanin production. Melanocytes... Read More
Autocrine signaling
Autocrine Signaling Definition What is autocrine signaling? Autocrine signaling is a type of cell signaling wherein a cell... Read More
Millons reagent
Definition noun A reagent for use in Millon reaction test for detecting the presence of tyrosine and other phenolic... Read More
Pheomelanin
Definition noun A type of melanin pigment that is made up of benzothiazine units and is responsible for yellow and pink to... Read More
Phenylalanine
phenylalanine (Science: amino acid) One of the amino acids which the body cannot manufacture itself, but must acquire from... Read More
Neuromelanin
Definition noun A type of melanin pigment present in parts of the brain, particularly in the neurons of substantia nigra and... Read More
Principles of Hormonal Control Systems
Hormones are chemical messengers that enter the blood directly upon their secretion from endocrine glands. A single gland or... Read More
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
Glycosylation
Definition noun A biochemical process where a glycan attaches to a protein, a lipid, or other organic molecule, especially... Read More
Autophosphorylation
Definition noun (biochemistry) The phosphorylation of the kinase through its own enzymatic... Read More
Morners test
Morner's test For cysteine, which gives a brilliant purple colour with sodium nitroprusside; for tyrosine, which gives a... Read More
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis Definition Phagocytosis is a basic physiological cellular process wherein a cell ingests a solid particle... Read More
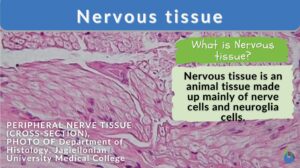
Nervous tissue
Nervous Tissue Definition Nerve cells (or neurons) and their associated cells, such as neuroglia cells, make up nervous... Read More
Polysaccharide
Polysaccharide Definition Biology Definition: A polysaccharide is a carbohydrate formed by long chains of repeating units... Read More
Hypomelanism
All the body cells of living organisms bear some color due to one or the other pigment molecule or complex. The pigment can... Read More
Genetic Mutations
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D.Genetic Mutations Genetic mutations are inherited variations in an... Read More
Amino acid
Definition noun, plural: amino acids (1) A molecule consisting of the basic amino group (NH2), the acidic carboxylic group... Read More
Genetic Control – On and Off Genes
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D.This lesson looks at the various factors involved that affect growth and... Read More
Oligosaccharide
Carbohydrates are organic compounds consisting of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, usually in the ratio of 1:2:1. They are one... Read More
Polypeptide
Polypeptide Definition Biology What are polypeptides? A polypeptide is defined as a polymer of amino acids joined together... Read More
photobiology
Photobiology Definition Photobiology, the biology of light, is a subdiscipline in biology. It focuses on the effects of... Read More
Spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis Definition Spermatogenesis is the biological process of producing sperm cells. It occurs in the male gonad... Read More
Sh domains
SH domains (Science: molecular biology) src homology domains: domains of protein that, from their homology with src are... Read More