Search Results for: vacuole
Contractile vacuole
Definition noun, plural: contractile vacuoles (cell biology) A specialized vacuole of eukaryote cells, especially protozoa,... Read More
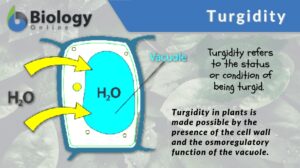
Turgor pressure
In biology, turgor pressure pertains to the pressure that is exerted by the fluid (e.g. water) against the cell wall. It is... Read More
Plant Cells vs. Animal Cells
Plant Cells Most cells are not visible with the naked eye. However, with microscopes of various types, plant cells can be... Read More
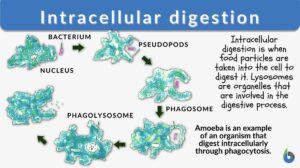
Intracellular digestion
Intracellular Digestion Definition What is intracellular digestion? ‘Intra’ means "inside" and ‘cellular’ pertains... Read More
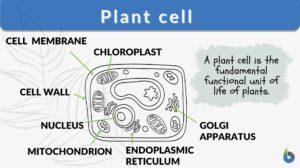
Plant cell
Plant Cell Definition A plant cell refers to any cell of a plant. It is the structural and functional unit of plants. Plant... Read More
Vacuolization
Definition noun, plural: vacuolizations The formation into, or multiplication of, vacuoles; being filled with... Read More
Cytopharynx
Definition noun, plural: cytopharynxes or cytopharynges The tube-like passageway in certain protozoans through which the... Read More
Lysosomal enzyme
Definition noun plural: lysosomal enzymes ly·so·somal en·zyme, ˈlaɪsəˌsoʊm əl ˈɛnzaɪm (biochemistry) Any of... Read More
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis Definition Phagocytosis is a basic physiological cellular process wherein a cell ingests a solid particle... Read More
Biological Cell Introduction
It only takes one biological cell to create an organism. In fact, there are countless species of single-celled organisms,... Read More
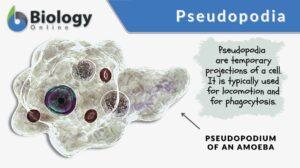
Pseudopodia
A pseudopodium (plural: pseudopodia) refers to the temporary projection of the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell. Pseudopodia... Read More
Endocytosis
Endocytosis Definition What is endocytosis in biology? Endocytosis is a cellular process by which a cell internalizes any... Read More
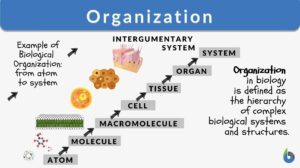
Organization
Organization Definition The meaning of the term "organization" is very simple. It means the state wherein things are... Read More
Animal cell
An animal cell is the fundamental functional unit of life of animals. It is also the basic unit of reproduction. Animal... Read More
Eukaryotic cells
Eukaryotic Cells Definition What is a eukaryotic cell? Eukaryotic cells refer to the cells of (or derived from) eukaryotes,... Read More
Phloem parenchyma
Definition noun The parenchyma cells in between the sieve tubes of the phloem, and functions primarily for food... Read More
Trophozoite
Definition noun, plural: trophozoites The active, amoeboid cell form that occurs during the feeding stage in the life cycle... Read More
Castration cells
Castration cells Altered basophilic cells of the anterior lobe of the pituitary that develop following castration; the body... Read More
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (sER) is part of or a region in the endoplasmic... Read More
Biological Cell Defense
Organisms must find a means of defense against antigens such a viruses described on the previous tutorial. If this was not... Read More