Search Results for: abnormal
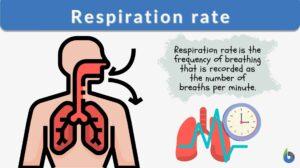
Respiration rate
Respiration Rate Definition Respiration rate is a vital life process that expresses the breathing rate in an organism... Read More
Spermiogenesis
Spermiogenesis Definition Spermiogenesis is the stage of spermatogenesis wherein the spermatids differentiate into mature... Read More
Chromatids
Chromatid Definition Chromatids are found inside our cells. Chromatids are condensed chromosomes distinguishable during... Read More
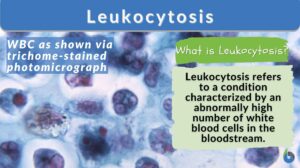
Leukocytosis
What Is Leukocytosis? Leukocytosis is a condition wherein the number of White Blood Cells (WBCs) is increased above the... Read More
Genetic Information and Protein Synthesis
Genetic Code Genes are sequences of DNA nucleotides that carry and transmit the information specifying amino acid sequences... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More
Diaphoresis
What is Diaphoresis? Diaphoresis is referred to excessive or profuse perspiration or sweating which may be due to... Read More
Hyperplasia
Hyperplasia (Science: pathology) The abnormal multiplication or increase in the number of normal cells in normal arrangement... Read More
Sphingolipidosis
Definition noun, plural: sphingolipidoses A lysosomal disease due to an abnormal sphingolipid... Read More
Myocardium
Myocardium Definition What is the myocardium of the heart? It is the muscular middle layer of the heart that is... Read More
Inbreeding
Inbreeding is a type of breeding or mating where closely related individuals with a common ancestor produce progenies with... Read More
Adipose tissue
Adipose Tissue Definition Adipose tissue, a specialized variety of connective tissue, is composed of lipid-rich cells known... Read More
Erythrocyte
Erythrocyte Definition Erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs) are the myeloid series of specialized cells that play an... Read More
Frameshift mutation
Define Frameshift Mutation What is a frameshift mutation? In biology, insertions or deletions of nucleotides in the coding... Read More
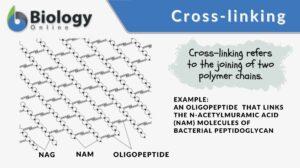
Cross-linking
Cross-linking Definition Cross-linking, in general, means the forming of cross-links between the joining structures. In... Read More
Decerebrate rigidity
Definition noun An involuntary posturing whereby the arms are extended on the sides while the head is arched back, as... Read More
Melanoderma
melanoderma 1. An abnormal darkening of the skin by deposition of excess melanin. 2. Hyperpigmentation of the skin by... Read More
An introduction to Homeostasis
Researched and Written by Jonjo MinnsSubmitted to biologyonline.com on February 25, 2009.Published in biologyonline.com... Read More
Pupillary light reflex
Definition noun, plural: pupillary light reflexes A reflex marked by the constriction of the pupil in response to the... Read More
Proto-oncogene
proto-oncogene (Science: molecular biology) The normal, cellular equivalent of an oncogene, thus usually a gene involved in... Read More
Symptomatic
Symptomatic Definition Symptomatic is a term that pertains to the observable manifestations or particular conditions... Read More
Polymorphism
Polymorphism Definition The occurrence of two or more different forms or morphs in the population of a species is referred... Read More
Respiration
Organization of the Respiratory System Each lung is composed of air sacs called alveoli - the sites of gas exchange with... Read More
Immune response
Immune Response Definition An immune response is defined as the reaction of the body in response to the presence of a... Read More
Chromosomes X and Y and Sex Determination
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D.In humans, the normal chromosome complement is 46, consisting of 22 pairs of... Read More
Established cell line
Established cell line --> cell line (Science: cell culture) a cell line is a permanently established cell culture that... Read More