Search Results for: base pair
Base pair substitution
Definition noun, plural: base pair substitutions A type of mutation involving replacement or substitution of a single... Read More
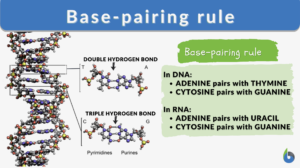
Base-pairing rule
Base-pairing Rules Definition The base-pairing rules are rules that apply during the pairing between one purine and one... Read More
Frameshift mutation
Define Frameshift Mutation What is a frameshift mutation? In biology, insertions or deletions of nucleotides in the coding... Read More
Chromosome
Chromosomes Definition Chromosomes are thread-like structures present in the nucleus of plant and animal cells. Chromosomes... Read More
Deoxyribonucleic acid
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds made up of linear... Read More
Translation
Translation, in general, is the conversion of something into another form, such as a word from one language to another. But... Read More
Transfer ribonucleic acid
Definition noun plural: transfer ribonucleic acids trans•fer ri•bo•nu•cle•ic ac•id, ˈtɹænsfɝ... Read More
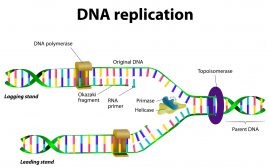
DNA Structure & DNA Replication
Previous pages in this tutorial have described the basics of a cell, the energy required by these cells and how energy is... Read More
Genetic variability
Genetic Variability Definition Genetic variability refers to the tendency of individual genetic characteristics in a... Read More
Transcription (biology)
In biology, transcription is the process of transcribing or making a copy of the genetic information stored in a DNA strand... Read More
Covalent bond
Covalent Bond Definition What is a covalent bond? In chemistry and other fundamental science fields, a covalent bond is... Read More
Genetic Information and Protein Synthesis
Genetic Code Genes are sequences of DNA nucleotides that carry and transmit the information specifying amino acid sequences... Read More
Microsatellite
Definition noun, plural: microsatellites (molecular biology) A tandem repeat ranging in length from 1 to 6 base pairs,... Read More
Recombination DNA repair
Recombination DNA Repair Definition Recombination DNA repair is a biological reparative process in response to DNA damage... Read More
Chemical Composition of the Body
In order to fully understand the mechanisms of human physiology, it is important to have an understanding of the chemical... Read More
Ribonucleic acid
Ribonucleic Acid Definition noun (uncountable), ribonucleic acids ri·bo·nu·cle·ic ac·id, raɪboʊnjuːkliːɪk... Read More
Polymorphism
Polymorphism Definition The occurrence of two or more different forms or morphs in the population of a species is referred... Read More
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid
Definition noun plural: ribosomal ribonucleic acids ri•bo•so•mal ri•bo•nu•cle•ic ac•id, ˈraɪ... Read More
Wobble hypothesis
wobble hypothesis (Science: molecular biology) explains why the base inosine is included in position 1 in the anticodons of... Read More
Silent mutation
A mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene or a chromosome. When there is only one nucleotide involved, it... Read More
Population Growth and Survivorship
By: Maria Victoria GonzagaPreviously, we learned about biodiversity and endemism. Now, let's look at the... Read More
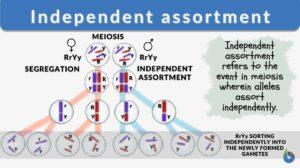
Independent Assortment
Independent Assortment Definition Independent assortment refers to the alleles or genes that sort into the newly formed... Read More
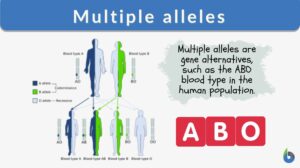
Multiple alleles
Alleles are the pairs of genes occupying a specific spot called locus on a chromosome. Typically, there are only two alleles... Read More
Substitution mutation
Definition noun, plural: substitution mutations (genetics) A small-scale mutation characterized by a substitution of one or... Read More
Repetitive DNA
Definition noun (molecular biology) Repetitive nucleotide sequences in the DNA throughout the genome Supplement The... Read More