Search Results for: catalyze
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
Transferase
Definition noun, plural: transferases (biochemistry) An enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a functional group from one... Read More
Oxidoreductase
Definition noun, plural: oxidoreductase (biochemistry) An enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of electrons from an electron... Read More
Polypeptide
Polypeptide Definition Biology What are polypeptides? A polypeptide is defined as a polymer of amino acids joined together... Read More
Anaerobic respiration
Anaerobic Respiration Definition What is anaerobic respiration? Anaerobic (cellular) respiration is a respiratory process... Read More
Splitting enzymes
splitting enzymes Enzyme's that, like aldolases, catalyze the conversion of a molecule into two smaller molecules without... Read More
Transposon
Definition noun, plural: transposons A small segment of DNA that is capable of replicating and inserting copies of DNA at... Read More
Methanotroph
Definition noun, plural: methanotrophs An organism that metabolize methane as a source of carbon and... Read More
White adipose tissue
Definition noun, plural: white adipose tissues A type of adipose tissue found in mammals used to store energy and acts as... Read More
Reducing enzyme
reducing enzyme --> reductase (Science: enzyme) An enzyme that catalyses a reduction; since all enzymes catalyze... Read More
Chemosynthesis
Definition noun, plural: chemosyntheses The production of a more complex chemical compound by combining two or more simpler... Read More
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation Definition We can define phosphorylation as a biochemical process in which a phosphate molecule is added to... Read More
Fermentation
Fermentation Definition What is fermentation? Fermentation is the breaking down of sugar molecules into simpler compounds... Read More
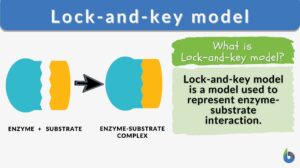
Lock-and-key model
Lock-and-key model Definition Lock-and-key model is a model for enzyme-substrate interaction suggesting that the enzyme and... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis Definition Biosynthesis refers to the production (synthesis) of a complex chemical compound from simpler... Read More